Figure 1.
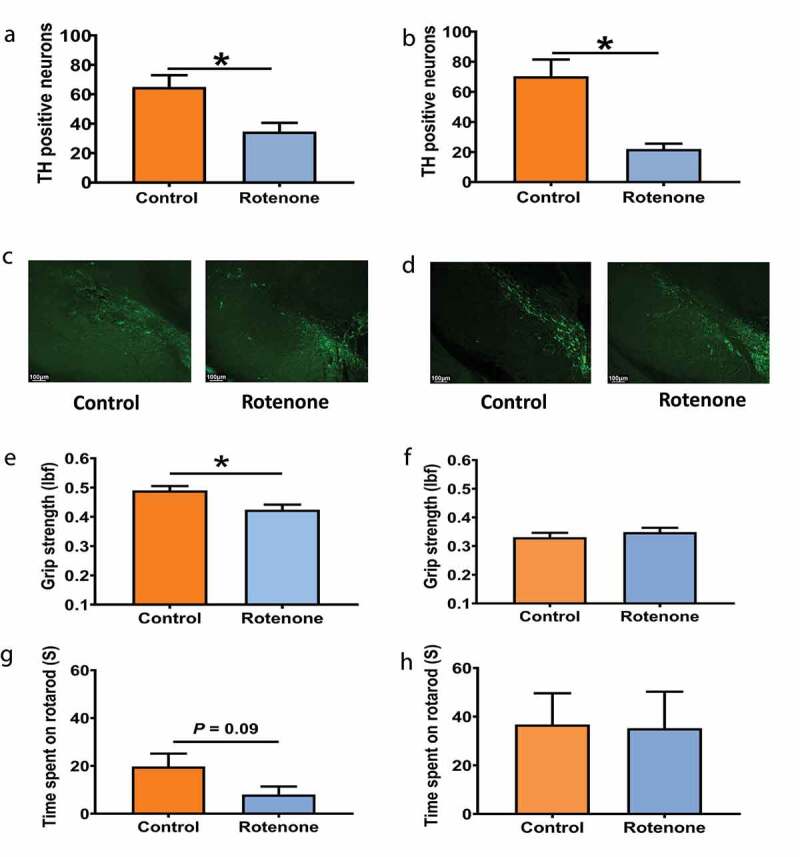
Chronic rotenone administration causes motor dysfunction in CR mice but not in GF mice. Change in TH-neuron number in substantia nigra following treatment with rotenone (10mg/kg) or vehicle with representative images in CR (A, C) and GF mice (B, D). Changes in grip strength and time spent in rotarod in CR mice (E, G) and GF mice (F, H) respectively following treatment with rotenone (10mg/kg) or vehicle. The data are presented as mean ± SEM [unpaired Student's t-test (two-tailed); *P <0.05]
