Figure 2.
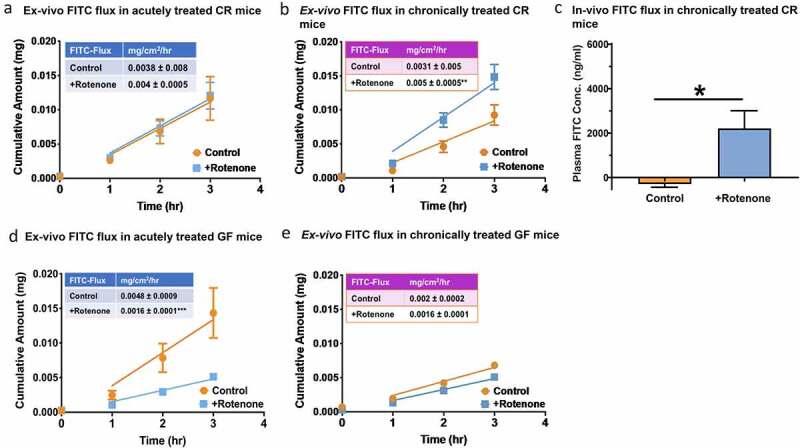
Chronic rotenone administration disrupts epithelial permeability and alters gut microbiota composition in CR mice. The cumulative fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC) flux across the ex-vivo colonic mucosal explants obtained from (A) acutely rotenone and vehicle treated CR mice and (B) chronically rotenone and vehicle treated CR mice. (C) In-vivo FITC flux in CR mice subjected to chronic rotenone and vehicle treatment. Ex-vivo FITC flux across colonic mucosal explants in (D) acutely rotenone and vehicle treated GF mice and (E) chronically rotenone and vehicle treated GF mice. The data is presented as mean ± SEM. Difference between the slopes are calculated by F-test; in chronically treated CR: DFn = 1, DFd = 20; **P<0.01 and in acutely treated GF: DFn = 1, DFd = 28; **P<0.01. Plasma absorption of orally administered FITC in chronically vehicle control versus rotenone treated CR mice [Student’s t-test (two-tailed); *P <0.05]
