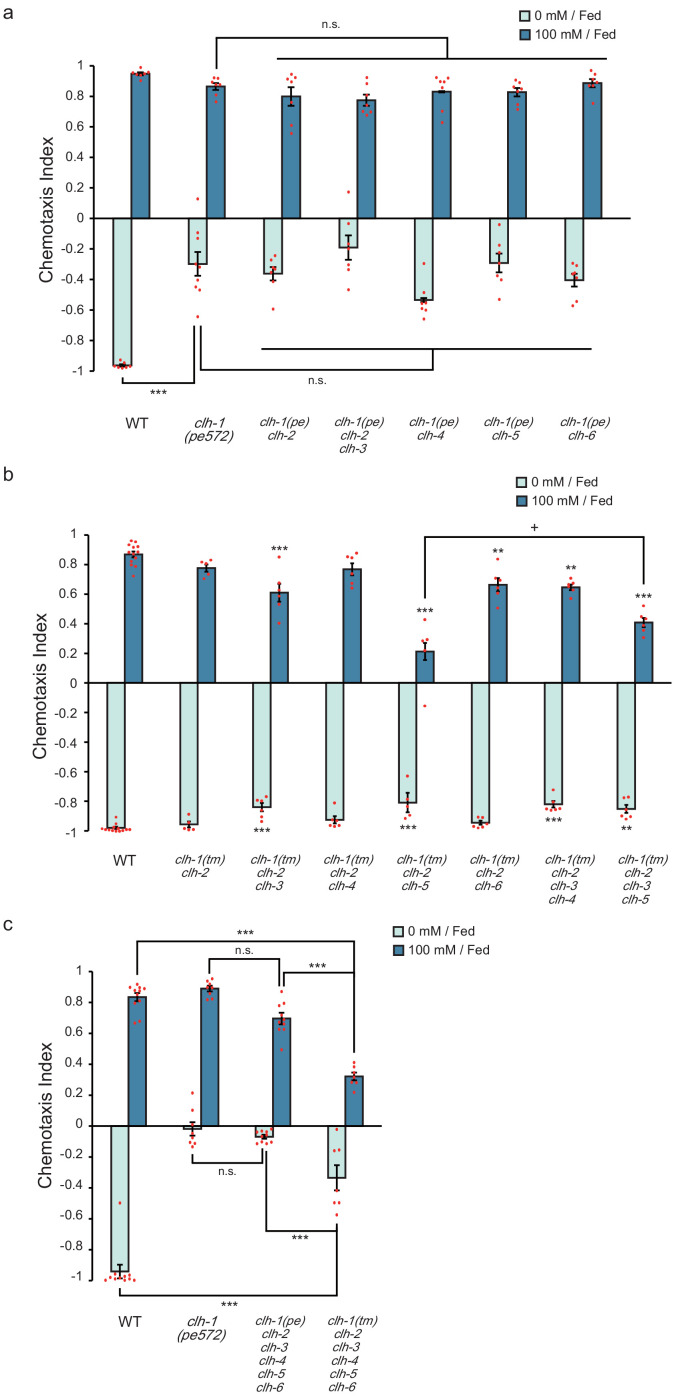
Figure 2. ClC genes redundantly function in salt chemotaxis.
(a) Chemotaxis of clh multiple mutants that carry clh-1(pe572) mutation with a deletion in other clh genes. Dots represent individual trials. Bars and the error bars represent mean +/- s.e.m., n ≧ 6 assays, Tukey’s test, ***p<0.001, n.s. not significant. (b) Chemotaxis of clh multiple mutants that carry clh-1(tm1243) mutation and a deletion in other clh genes. Dots represent individual trials. Bars and the error bars represent mean +/- s.e.m., n ≧ 5, Tukey’s test, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, compared with wild type. +p<0.05, compared with indicated mutants. (c) Chemotaxis of clh hexatruple mutants. Dots represent individual trials. Bars and the error bars represent mean +/- s.e.m., n ≧ 7, Tukey’s test, ***p<0.001, n.s. not significant.