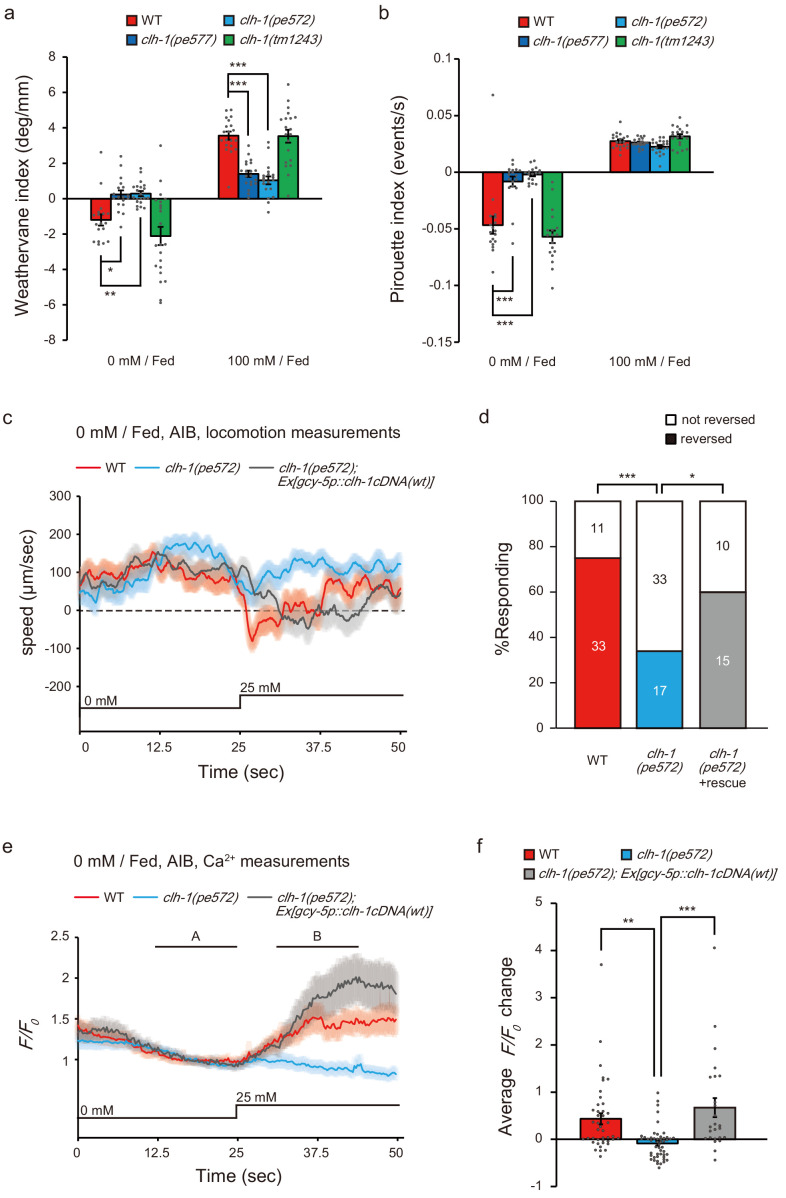
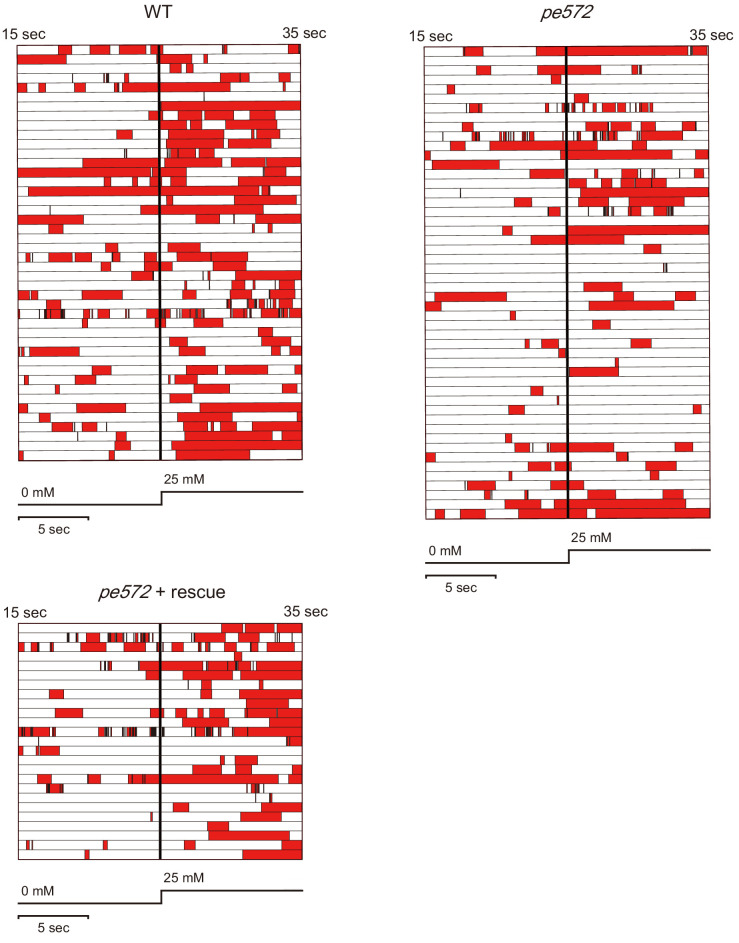
Figure 6. Missense mutations in clh-1 attenuate both klinotaxis and klinokinesis, as well as AIB response and reversal in response to salt increase.
(a and b) clh-1(pe) mutants show defects in migration bias in salt chemotaxis. Bias of klinotaxis (a) and klinokinesis (b), represented by weathervane index and pirouette index, respectively. In both mechanisms, positive and negative values indicate migration bias toward higher and lower salt concentrations, respectively. Bars and the error bars represent mean +/- s.e.m., dots represent individual trials. n ≧ 18 assays, Dunnett’s test, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01, *p<0.05. (c and e) Locomotion speed of animals (c) and calcium responses of AIB (e) after cultivation at 0 mM NaCl in the presence of food. In panel (e), A and B indicate the time points for calculation of F/F0 changes. NaCl concentration change from 0 mM to 25 mM at 25 s. The shaded region represents s.e.m., n ≧ 25 animals. (d) Proportion of animals that showed reversal after salt stimulus. Reversal was defined as follows; backward locomotion, whose velocity less than −100 µm/sec was continued for more than 1 s (35 frames). The error bars represent s.e.m., n ≧ 25 animals, Fisher’s exact test. ***p<0.001, *p<0.05. (f) F/F0 change upon salt stimulus (B - A, see Materials and methods for details). Bars and the error bars represent mean +/- s.e.m., dots represent individual trials. n ≧ 25 animals, Tukey’s test, ***p<0.001, **p<0.01.
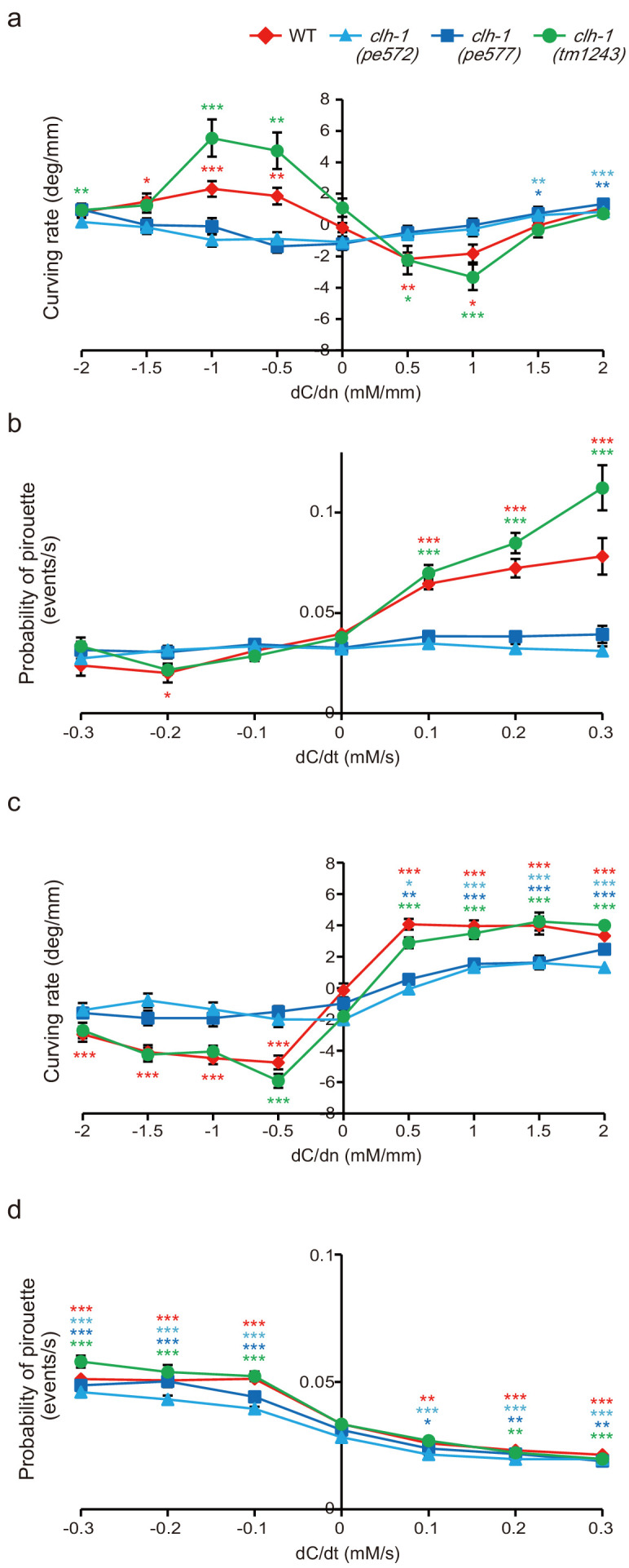
Figure 6—figure supplement 1. Quantification of the navigation behaviors.