Figure 2.
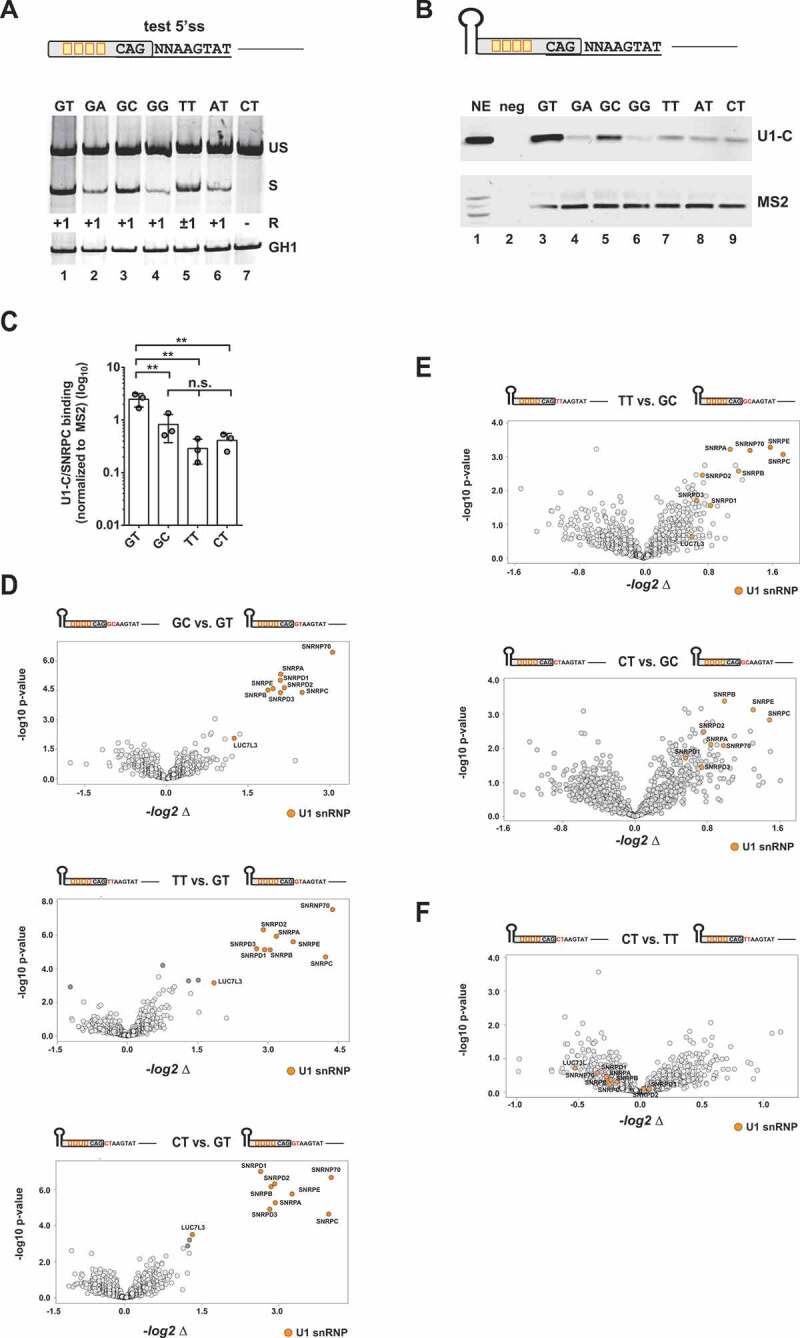
Binding of U1 snRNP-associated proteins to noncanonical splice sites
(A) Assessment of the usage of different noncanonical splice sites using an HIV-1-based SV-env/eGFP splicing reporter [23], which contains four enhancer binding sites upstream of the 5’ss test sequence CAGNNAAGTAT. HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with 1 µg of each: the respective SV-env/GFP splicing reporter and pXGH5 (expressing human growth hormone 1 [GH1] to monitor equal transfection efficiencies). RNA was isolated 30 h post-transfection and used for RT-PCR analysis as described in Material&Methods. Different splicing positions (R) obtained by sequencing of the RT-PCR products are indicated below the gel image. US: unspliced; S: spliced; +1: exclusive cleavage at position +1; −1/+1: cleavage at positions −1 and +1; +1/5: cleavage at positions +1 and +5. (B, C) RNA in vitro binding assays show U1-C/SNRPC binding to noncanonical 5’ss. As mentioned before, in vitro transcribed RNAs were equipped with an MS2 binding site at the 5ʹ-end bound by recombinant MS2 coat protein that had been added to the nuclear extracts (NE). RNAs were immobilized and analysed for binding of U1-C/SNRPC (U1 snRNP) and MS2 (precipitation control). Signal intensities were quantified by ImageJ and normalized to the mean band intensity of U1-C/SNRPC for each biological replicate (n = 3). Data show the mean value ± standard deviation (SD). ** p < 0.01 and n.s: not significant (one-way ANOVA). (D, F) Comparative MS analysis of the protein fractions eluted from the different in vitro RNA substrates largely agreed with a positive correlation between U1 snRNP protein precipitation efficiency and 5’ss usage. Vulcano Plots were created using InstantClue (www.instantclue.uni-koeln.de). U1 snRNP proteins are highlighted in orange. Significantly enriched proteins are highlighted in dark grey and dark orange (U1 snRNP). Dinucleotides are highlighted in red.
