Figure 3.
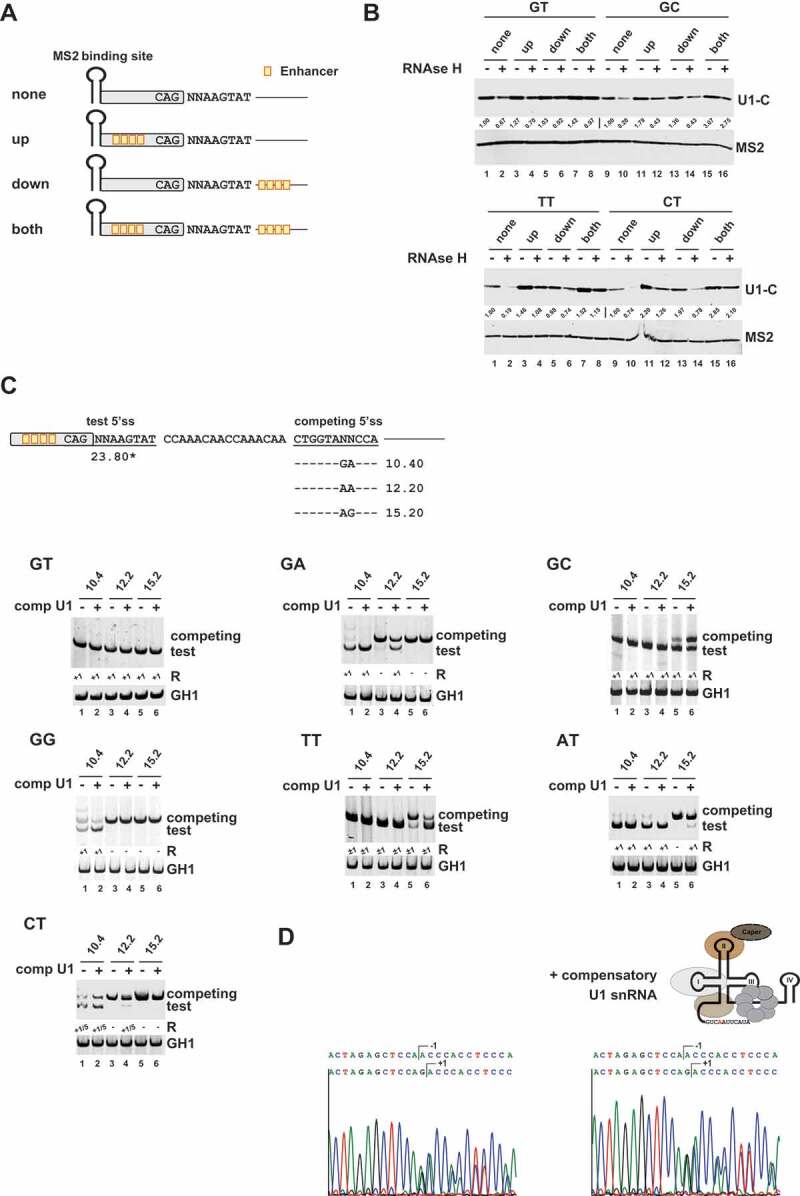
U1 snRNP binding to noncanonical splice sites relies on stable U1 RNA duplex formation
(A) Schematic of the RNA substrates used for RNA in vitro pulldown assays. Enhancer sites are indicated by orange boxes. (B) RNA in vitro pulldown assays showed that base pairing interactions with the U1 snRNA and splicing enhancers are major determinants for U1-C/SNRPC binding to noncanonical 5’ss sequences. HeLa cell nuclear were depleted (+) or mock-depleted (-) of U1 snRNA 5ʹ-end using short DNA oligonucleotides and RNase H. RNA pulldown assays were performed as described before. MS2 coat protein served as control. Signal intensities were quantified using the ImageJ software (https://fiji.sc/). The MS2 protein band intensities were used to normalize the U1-C/SNRPC signals. The normalized U1/C/SNRPC band intensities of the enhancer-less splice site substrates were set to 1 (‘none’, RNase H -) to calculate relative changes caused by RNase H treatment and/or presence of enhancer sequences in the upstream exon (‘up’) or downstream intron (‘down’). (C) Schematic of the HIV-1-based SV-env/eGFP splicing reporter containing the different pairs of competing splice sites (on top). Sequence variations (denoted by ‘NN’) and H-Bond scores (https://www2.hhu.de/rna/html/H-Bond_score.php) of the competing canonical splice sites are indicated below. The different splicing reporters were either coexpressed with a compensatory U1 snRNA (+) or not (-). RT-PCR analyses of spliced reporter mRNAs were performed as described before. Splicing positions (R) are indicated below.*: H-Bond score had been calculated by inserting a GT at position +1/+2; +1: cleavage at position +1; −1/+1: cleavage at positions −1 and +1; +1/5: cleavage at positions +1 and +5. (D) Sequencing results of TT splice site usage in the presence and absence of a compensatory U1 snRNA. Polyacrylamide (PAA) bands were isolated, reamplified with primer pair #3210/#3211 and sent to sequencing analysis using primer #3210.
