Figure 4.
U1 snRNP binding act as splicing enhancer themselves
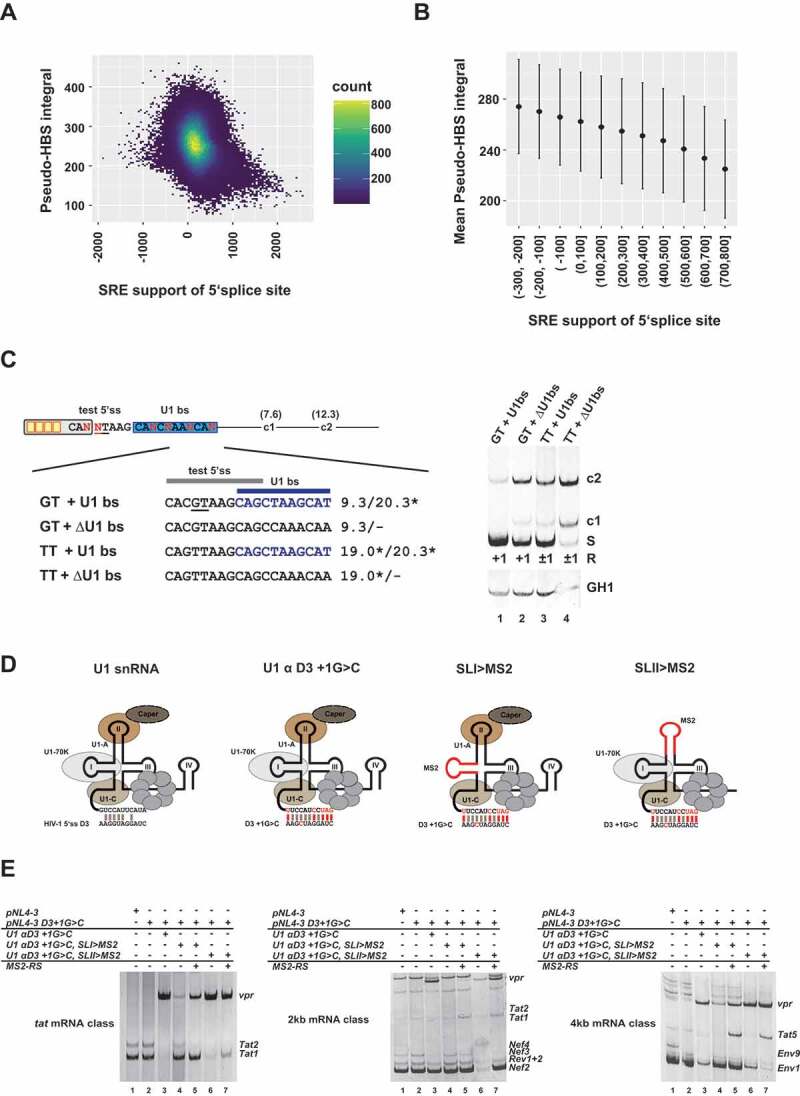
(A, B) Splicing regulatory element (SRE) support and Pseudo-HBS score integral of 50nt downstream sequence. (A) The density scatter plot illustrates each SRE support/‘Pseudo’-H-Bond score integral (Pseudo-HBS integral) pair grouped in small bins. Yellow colored bins indicate a high number of 5’ss with a specific SRE to Pseudo-HBS integral. (B) Mean Pseudo-HBS integral and standard deviation of SRE support groups. (C) U1 binding sites promote the activation of weak canonical and noncanonical 5’ss. Usage of a weak GT splice site (HBs: 9.30) and a noncanonical TT site (HBs: 19.0*) was tested in the presence or absence of a non-functional U1 binding site (U1 bs, HBs: 20.3*, highlighted in blue). Splicing positions (R) are indicated below.*: H-Bond score had been calculated by inserting a GT at position +1/+2; S: spliced; +1: cleavage at position +1; −1/+1: cleavage at positions −1 and +1; c1 and c2: cryptic splices sites in the downstream intron. (D) Schematic of the U1 snRNA mutants used in (E). (E) RT-PCR analysis show that RS domain binding to stem loop I of the U1 snRNA is important for exon-definition. HEK293T cells were transiently transfected with each of the proviral plasmids and U1 and/or MS2-RS fusion protein-expressing plasmids as indicated above the gel images. HIV-1 mRNA species are indicated to the right of the gel images according to the nomenclature published previously [63].
