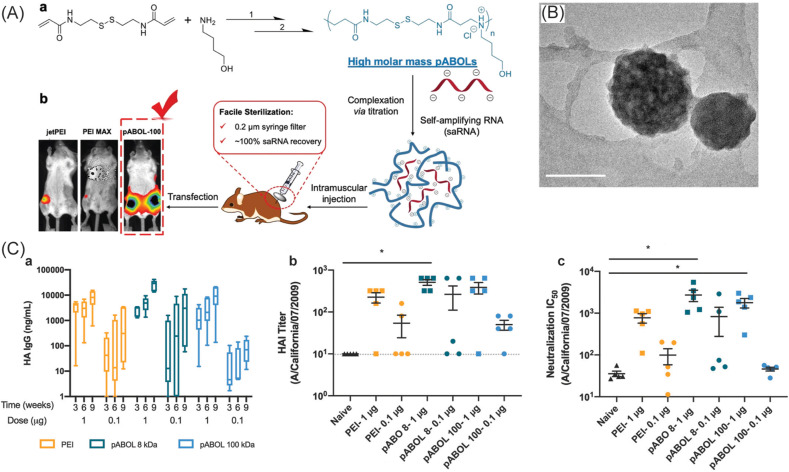
Fig. 6.
Polymeric nanoparticle vaccines against H1N1 influenza virus. The nanoparticles are composed of a complex between linear, cationic polymer poly(N,N-cystaminebis(acrylamide)-co-4-amino-1-butanol (pABOL) and self-amplifying RNA (saRNA) encoding hemagglutinin (HA) antigen from the H1N1 A/California/07/2009 strain. (A) Synthesis of pABOL through aza-Michael polyaddition of 4-amino-1-butanol to N,N-cystaminebis(acrylamide) catalyzed by triethylamine (a), and its subsequent ionic complexation with saRNA, and high transfection efficiency of the formed nanoparticles as compared to poly(ethyleneimine) (PEI) based nanoparticles (b). (B) Typical TEM image of pABOL-saRNA nanoparticles stained with 2% uranyl acetate (scale bar: 100 nm). (C) Immunogenicity of the nanoparticles at different pABOL molecular weights and saRNA doses after intramuscular vaccination of mice: HA-specific IgG titer (a), HA inhibition (HAI) titer of Cal/09 flu virus (b), and neutralization IC50 against Cal/09 flu virus (c). Reproduced with permission from Refs. [127]. Copyright (2020) American Chemical Society.