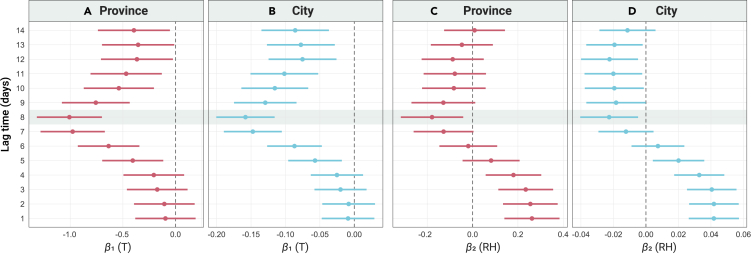
Figure 2.
Ambient Temperature & Relative Humidity and COVID-19 Transmission
Associations of ambient temperature (A, province level; B, city level) and relative humidity (C, province level; D, city level) with the transmission rate of COVID-19. Transmission rate was defined as the increased rate of cumulated confirmed cases per day in a logistic growth model: Equation (1). The regression coefficients (β1 and β2) were obtained using a linear mixed-effect model as follows: R[t, s]= β1Tt+ β2RHt+ β3WSt + β4PRt+ β5MIIt+ β6MOIt+ β7PDt + γ(L). This formula incorporated seven fixed terms (β1-7) to model the effects of temperature (T), relative humility (RH), wind speed (WS), precipitation (PR), population mobility indexes of moving-in (MII) and moving-out (MOI), population density (PD), and a random intercept (γ) to control for the location (L)-specific effects. Data are shown with an estimated value with 95% confidence interval.