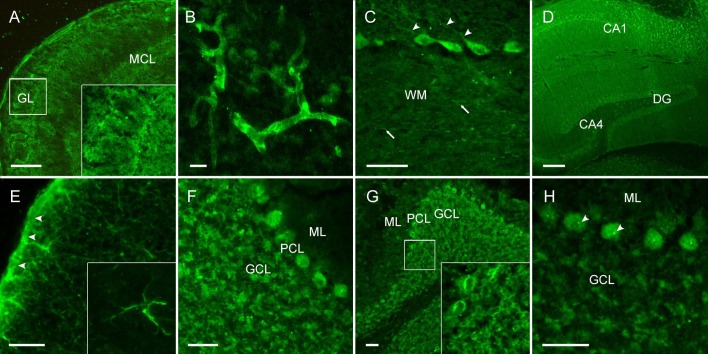
Fig. 1.
CSF of COVID-19 patients shows strong IgG autoreactivity on unfixed mouse brain sections. Representative images of indirect immunofluorescence demonstrate autoantibody binding to circumscribed anatomical structures including (A) neuropil of the olfactory bulb, (B) medium-sized vessels in the brain, (C) proximal dendrites of Purkinje neurons (arrowheads) and myelinated fibers (arrows) in the cerebellum, (D) neuropil in the hippocampus, (E) glia limitans (arrowheads) and astrocytes (enlarged box) throughout the brain. Several autoantibodies target intracellular antigens, such as (F) densely clustered intraneuronal epitopes, (G) perinuclear antigens or (H) nucleoli (arrowheads) as part of an anti-nuclear antibody response.