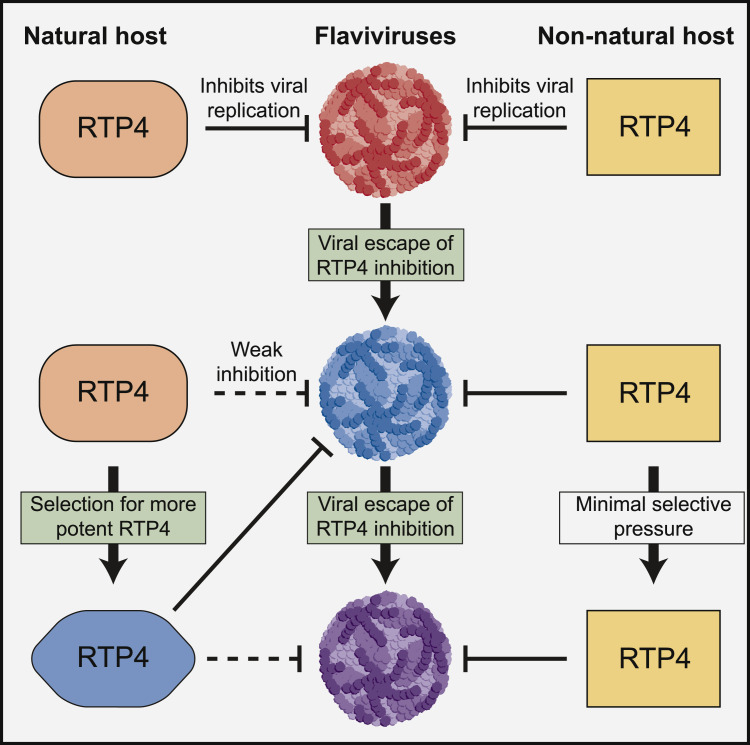
Figure 1.
An Evolutionary Arms Race between Flaviviruses and RTP4
Flaviviruses replicate in their natural host species, but non-natural host species also may be exposed to infection, for example through a mosquito or tick bite. Boys et al. found that the antiviral effector RTP4 inhibits flaviviruses in a species-specific manner, with RTP4 orthologs from natural hosts being less potent against particular flaviviruses than orthologs from non-natural hosts. Their work suggests a molecular arms race, wherein RTP4 inhibits flavivirus replication, creating selective pressure for flaviviruses to evolve to antagonize RTP4 in their natural hosts, and in turn pressuring RTP4 to evolve greater potency against the specific flaviviruses that target that host.