Figure 2.
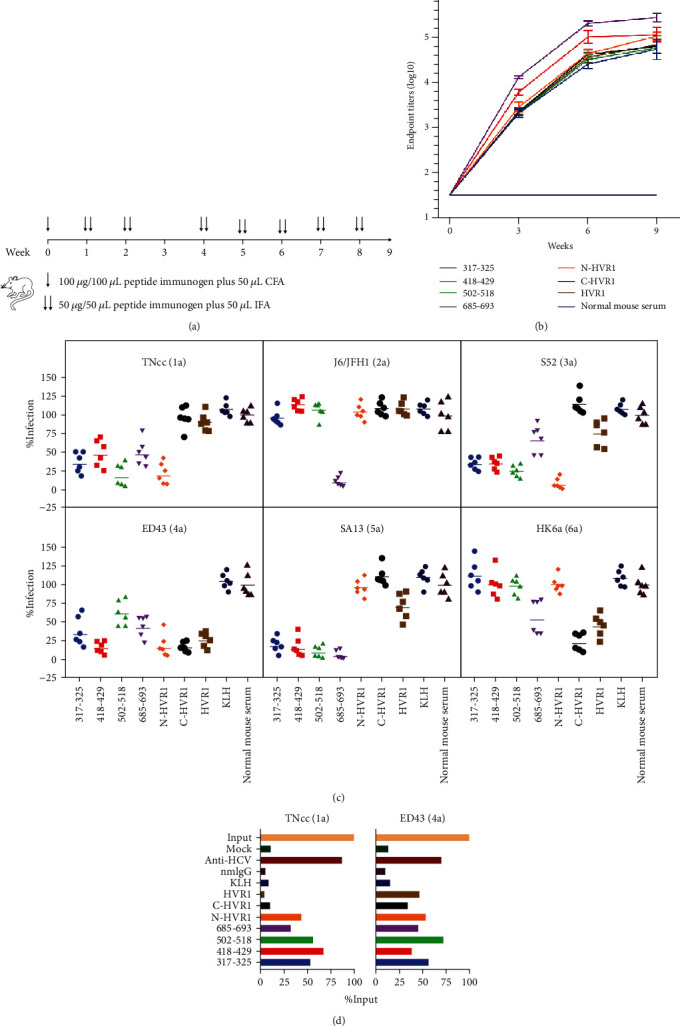
Humoral response induced by peptides. (a) Illustration of the immunization procedure. The peptide plus KLH protein, or PBS plus KLH protein, together with CFA or IFA, was inoculated into BALB/c mice at the indicated time points. (b) Kinetics of peptide-specific antibody titers of the antisera. The endpoint titers of antisera collected at weeks 0, 3, 6, and 9 were determined by ELISA. Sera from mice without immunization, defined as “normal mouse serum,” served as a baseline. The mean ± standard error of the mean (SEM) of each group is shown. (c) The antiserum of each mouse was diluted at 1 : 50, mixed with 100 FFU of HCVcc, and then added to naïve Huh7.5 cells. HCVcc without sera was added as a “mock” control. Seventy-two hours postinfection, the FFU was determined by an indirect immunofluorescence assay. The infection of “mock” was arbitrarily set to 100%, and the relative infection rates were calculated using GraphPad Prism 8 software. Each experiment was repeated in triplicate, and the representative data of 1 experiment is shown. The geometric mean of each group is displayed. (d) HCVcc TNcc(1a) or ED43(4a) stock (~106 IU as “input”) was precipitated with 2 μg/mL IgG-coated Protein G Beads. Normal mouse IgG (nmIgG) and IgG purified from a convalescent hepatitis C patient (anti-HCV) were used as the negative and positive controls, respectively. HCVcc nonspecifically binding to Protein G Beads without an IgG coating was defined as a “mock.” HCV RNA of virus precipitated with beads was determined by qRT-PCR.
