Figure 5.
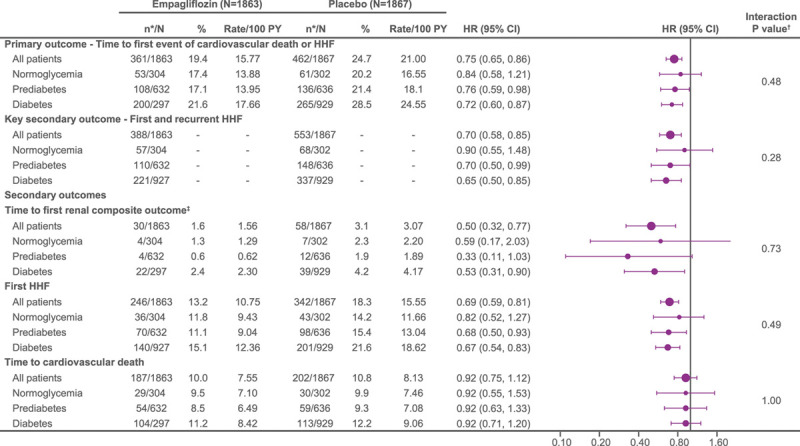
Treatment effect of empagliflozin vs placebo on primary and secondary outcomes in patients with normoglycemia, prediabetes, and diabetes. Recurrent event analyses are based on a joint frailty model accounting for competing risk of cardiovascular death. *n corresponds to number of events in recurrent event analyses and number of patients with event for time-to-first-event analysis. †Interaction P values from trend test assuming ordered categories. The trend test reflects an assumed ordering of the subgroups from normoglycemia to prediabetes to diabetes testing a linear trend across subgroups. ‡Composite renal end point: time to first event of chronic dialysis or renal transplant or sustained reduction of ≥40% estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR; Chronic Kidney Disease Epidemiology Collaboration [CKD-EPI]cr); or for patients with eGFR (CKD-EPI)cr ≥30 mL/min/1.73 m2 at baseline: sustained eGFR <15 mL/min/1.73 m2; for patients with eGFR (CKD-EPI)cr <30 mL/min/1.73 m2 at baseline: sustained eGFR <10 mL/min/1.73 m2. An eGFR (CDK-EPI)cr reduction is considered sustained if it is determined by 2 or more consecutive postbaseline central laboratory measurements separated by at least 30 days (first to last of the consecutive eGFR values). If there is no additional measurement ≥30 days after the eGFR reduction is observed and the patient dies within 60 days of this measurement, then the eGFR reduction is also considered sustained. HHF indicates hospitalization for heart failure.
