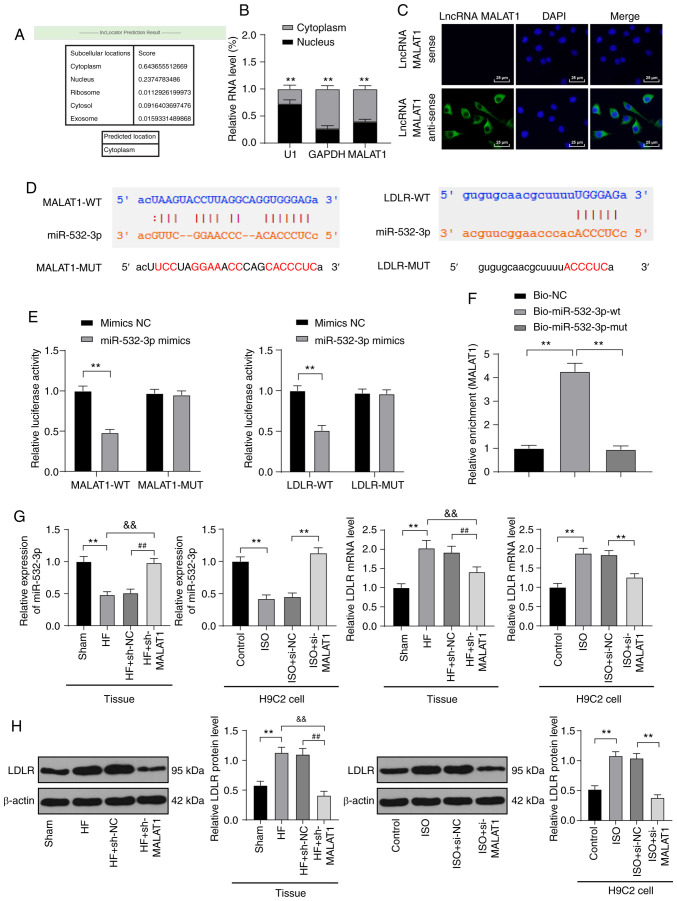
Figure 5.
LncRNA MALAT1 competitively bound to miR-532-3p to upregulate LDLR. (A) An online website predicted the sublocation of lncRNA MALAT1. (B) Localization expression of lncRNA MALAT1 was detected using nuclear and cytoplasmic fractionation assays. (C) The localization of lncRNA MALAT1 was observed using FISH assay; scale, 25 µm; (D). An online software predicted the binding sites between MALAT1 and miR-532-3p as well as miR-532-3p and LDLR. (E) In 293T cells, binding interaction between MALAT1 and miR-532-3p as well as miR-532-3p and LDLR was verified using dual-luciferase reporter gene assays. (F) Binding relationship between MALAT1 and miR-532-3p was verified using RNA pull-down assays. (G) miR-532-3p expression and LDLR mRNA levels in rat tissues and H9C2 cells were detected using RT-qPCR, n=4. (H) LDLR protein levels in rat tissues and H9C2 cells were detected using western blot analysis, n=4. Three independent repeated tests were conducted. The data were expressed as the mean ± standard deviation and analyzed using one-way or two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test. **P<0.01, compared with the sham group or the control group or the ISO + si-NC group; &&P<0.01, compared with the HF group; ##P<0.01, compared with the HF + sh-NC group.