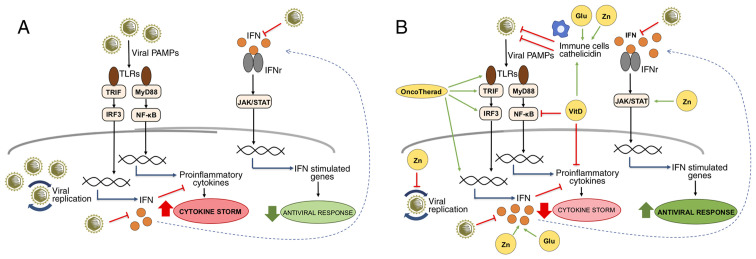
Figure 1.
IFN-related signaling pathways modulated by OncoTherad, zinc, vitamin D and glutamine during viral infections. (A) Viral PAMPs are recognized by TLRs, triggering signaling pathways mediated by TRIF and MyD88. The TRIF/IRF3 pathway activates the expression of IFNs that, when interacting with their receptors, activate the JAK/STAT pathway and the expression of genes with important antiviral functions. On the other hand, the MyD88/NF-κB pathway is responsible for the expression of pro-inflammatory genes, such as cytokines, which, when in excess, contribute to the cytokine storm characterized by uncontrolled inflammation. SARS-CoV-2 is known for inducing cytokine storm associated with severe forms of COVID-19, as well as for inhibiting the production of IFNs and evading the IFN-related antiviral defense system. (B) The compounds OncoTherad, zinc, vitamin D and glutamine can contribute to the organism's antiviral defenses by several mechanisms: OncoTherad increases the TLR4/TRIF/IRF3/INF signaling pathway; zinc inhibits viral replication, activates STAT1, stimulates IFN production and induces the antiviral responses mediated by IFN-stimulated genes; vitamin D inhibits NF-κB and the expression of its pro-inflammatory target genes, as well as stimulates immune cells and the expression of catelicidin with antiviral activity; and glutamine is essential for the proliferation of immune cells and the production of IFN. Together, these compounds can help to attenuate inflammation associated with the cytokine storm and to increase the organism's antiviral status. The green arrows represent activation, the red truncated lines indicate inhibition and the blue arrows indicate activation of gene expression. Glu, glutamine; IFN, interferon; IFNr, interferon receptor; JAK/STAT, Janus-activated kinase/signal transducer and activator of transcription proteins; MyD88, myeloid differentiation factor 88; NF-κB, nuclear factor-κB; PAMP, pathogen-associated molecular pattern; TLR, Toll-like receptor; TRIF, Toll/IL-1 receptor domain-containing adaptor inducing IFN-β; VitD, vitamin D; Zn, zinc.