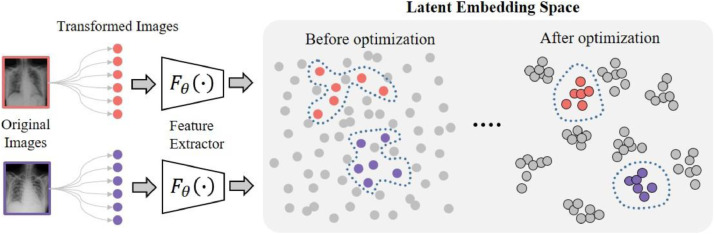
Fig. 3.
Illustration of the effect of contrastive learning. We use different colors to distinguish different samples. Each image is transformed by a series of augmentation operations, and the feature extractor projects the transformed images to the latent embedding space. Contrastive learning is used to optimize the model for better spatial aggregating properties: representations belonging to a same image are concentrated together to formulate semantic clusters, whereas representations belonging to different images are scattered across the latent embedding space. (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)