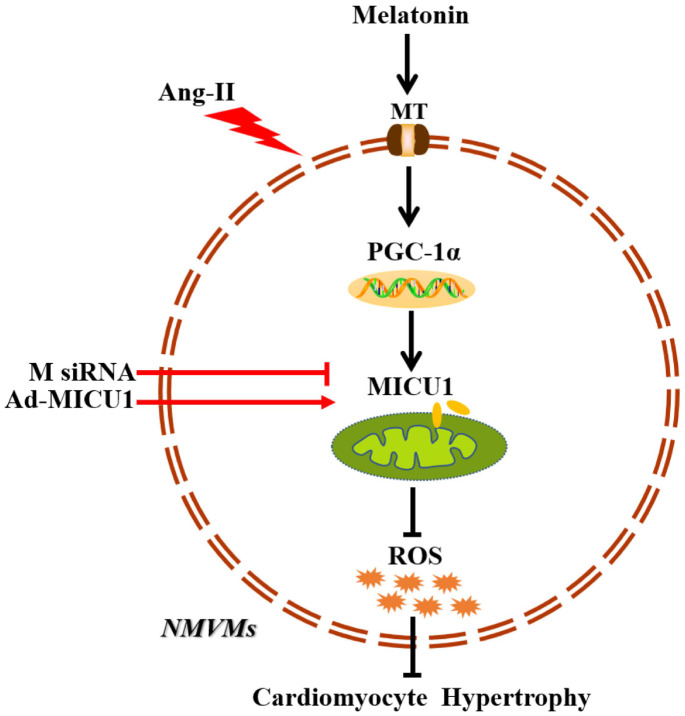
Figure 9.
Schematic diagram depicts that melatonin ameliorates cardiac hypertrophy by activating MICU1. As located in the intermembrane space of mitochondria, MICU1 is responsible for maintaining mitochondrial homeostasis. Exposure to Ang-II, MICU1 is significantly downregulated in NMVMs. With genetic methods, we found that MICU1 reduction in cardiomyocytes leads to mitochondrial dysfunction, enhances ROS overload and subsequently aggravated cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, but not in MICU1 overexpression NMVMs. As a therapeutic agent, melatonin is able to increase MICU1 expression via activating PGC-1α to maintain mitochondrial homeostasis and attenuate ROS overload, consequently ameliorated cardiomyocyte hypertrophy. MT, melatonin receptor; MICU1, mitochondrial calcium uptake 1; PGC-1α, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-γ coactivator-1α; ROS, reactive oxygen species; NMVMs, neonatal mice ventricular myocytes; M siRNA, MICU1-specific siRNA; Ad-MICU1, recombinant adenovirus encoding MICU1.