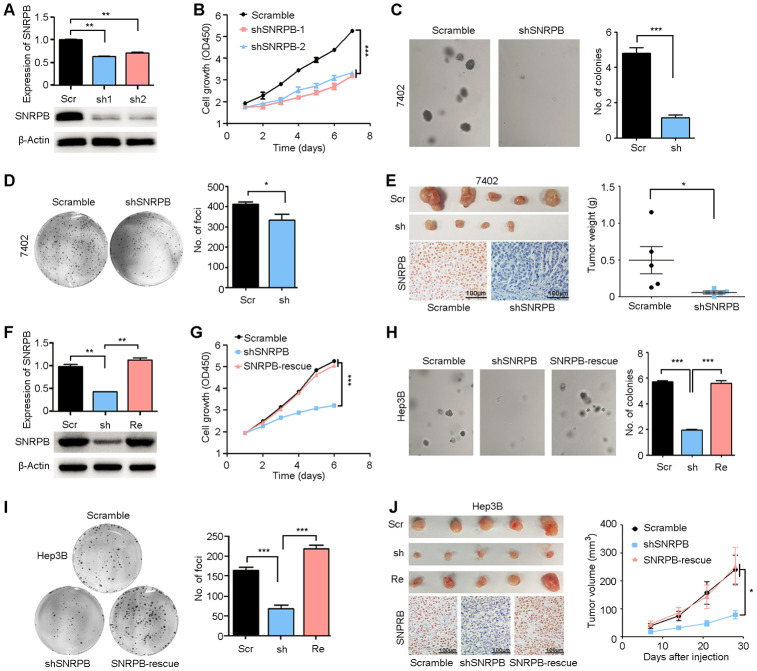
Figure 3.
Silencing SNRPB inhibits HCC cell growth in vitro and in vivo. (A) qRT-PCR and western blotting analyses indicating the silencing of SNRPB with shRNAs (shSNRPBs) in 7402 cells. 18S or β-Actin served as the loading control. (B) XTT assay showing that the cell growth rate of 7402 cells was inhibited by shSNRPB. (C) Representative images of decreased colony formation induced by shSNRPB in soft agar assays. The results are summarized in the right panel. (D) Representative image of foci formation in monolayer culture of 7402 cells with silenced SNRPB. The numbers of foci are summarized in the right panel. (E) Images of the xenograft tumors formed in nude mice injected with shSNRPB- and scramble-transfected cells. The weights of xenograft tumors are summarized in the right panel. IHC staining was performed to confirm the expression of SNRPB in xenograft tumors (lower panel). Scale bars = 100 μm. (F) qRT-PCR and western blotting analyses showing the expression levels of SNRPB in Hep3B cells transfected with SNRPB-shRNA (shSNRPB) and SNRPB-overexpressing vector for rescue (SNRPB-rescue). 18S or β-Actin served as the loading control. (G–I) Cell growth curves (G), colony formation (H) and foci formation (I) assays showed that transfection with SNRPB could rescue the cell growth inhibited by shSNRPB in Hep3B cells. (J) Images of the xenograft tumor formed in nude mice injected with scramble vector-, shSNRPB- and SNRPB-rescue-transfected cells. The volume curves of xenograft tumors are summarized in the right panel. IHC staining was performed to confirm the expression of SNRPB in xenograft tumors (lower panel). Scale bars = 100 μm.