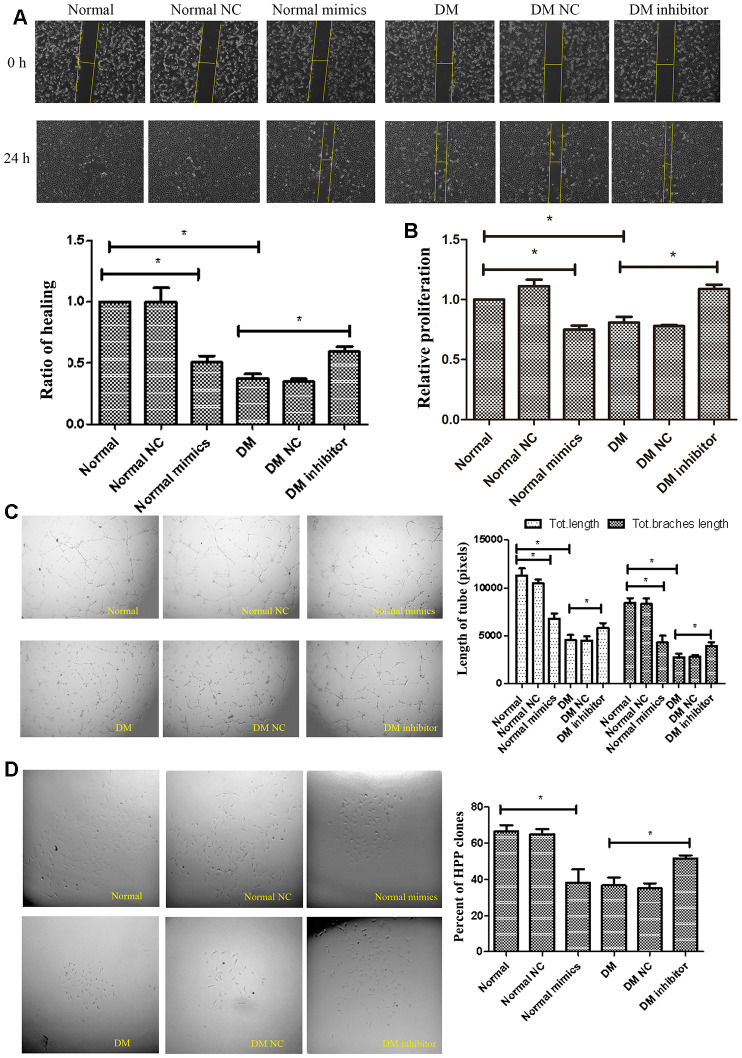
Figure 3.
MiR-139-5p inhibits the function of ECFCs. (A, B) Migration and proliferation of normal ECFCs transfected with miR-139-5p mimics and DM ECFCs transfected with miR-139-5p inhibitors were assessed. The photos were captured by a 40X microscope and the statistics performed by Image J. (N=3) *P < .05 versus normal or diabetic ECFCs. (C) Tube formation of normal ECFCs transfected with miR-139-5p mimics and DM ECFCs transfected with miR-139-5p inhibitors were assessed. The photos were captured by a 40X microscope and the statistics performed by Image J. (N=3) *P < .05 versus normal or diabetic ECFCs. (D) The cloning ability of normal ECFCs transfected with miR-139-5p mimics and diabetic ECFCs transfected with miR-139-5p inhibitors were detected using single cell clone experiments. (N=3) *P < .05 versus normal or diabetic ECFCs. Data shown in the graphs represent mean ± standard deviation.