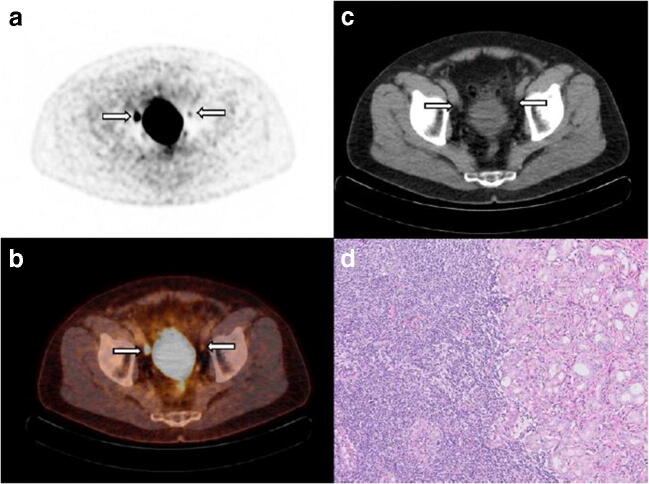
Fig. 3.
A 68-year-old man with cT2c, Gleason score 3 + 4 = 7 prostate cancer and initial PSA 10.4 ng/mL considered candidate for radical prostatectomy with extended pelvic lymph-node dissection. MSKCC nomogram showed 10.8% risk of lymph-node involvement. Transversal 18F-DCFPyL PET (a) and fused PET/CT (b) show intense uptake in the pelvic region right, corresponding with an enlarged 10-mm lymph node adjacent to the right external iliac artery on CT (c), suspect for lymph-node metastasis (a–c, left arrow). A contralateral focus with faint uptake is observed on PET and fused PET/CT in the pelvic region, without an evident morphologic substrate on CT. Due to the minimal tracer uptake (above the blood pool and lower than the liver); this left-sided focus was not suspect for lymph-node metastasis after dual reading. After surgical resection of 26 lymph nodes, post-operative histopathology revealed a right-sided right iliac lymph-node metastasis measuring 10 mm, as well as a left iliac lymph-node metastasis of 5 mm, haematoxylin and eosin stain, original magnification × 10 (d)