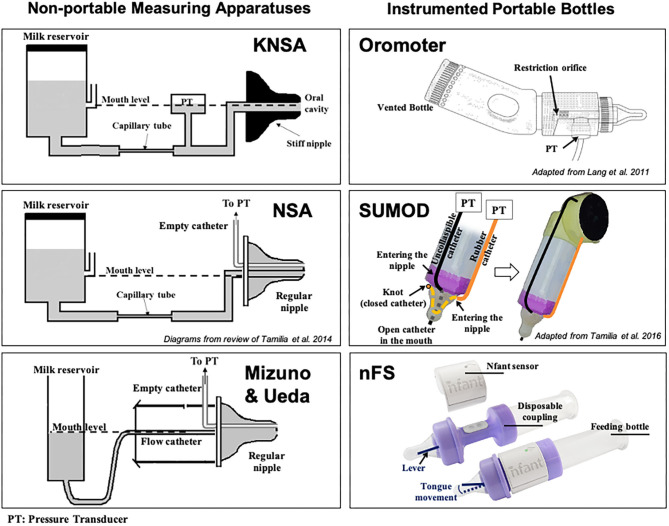
Figure 7.
Technological solutions to assess neonatal sucking. Schematic diagrams of some technological solutions used to measure sucking during bottle feeding in infants. (Left) Non-portable measuring apparatuses [KNSA (77), NSA (79), and Mizuno-Ueda system (80)]: pressure transducers (PTs) are used to measure sucking pressures exerted on a nipple, which is not connected to a regular feeding bottle, but to a reservoir containing milk via a flow-regulating capillary tube or regular catheter. The milk reservoir is always kept at the mouth level to eliminate net hydrostatic pressure (unlike in regular bottle-feeding sessions). Regular nipples were used in NSA and Mizuno & Ueda's systems, while a stiff nipple was used in KNSA. (Right) Portable measuring solutions: feeding bottles instrumented with pressure transducers (PTs) to measure different sucking pressures [Orometer (81) and SuMOD (82): via air-filled catheters] or tongue movement (nFS; via a lever). These solutions were designed to be attached to regular bottles for easy use in clinical settings. Orometer measures the suction component of sucking; nFS measures tongue movement (related to the expression component); while SuMOD measures suction and expression components separately (enabling coordination assessment). nFS is a wireless solution, while Orometer and SuMOD require wired connection to an acquisition system.