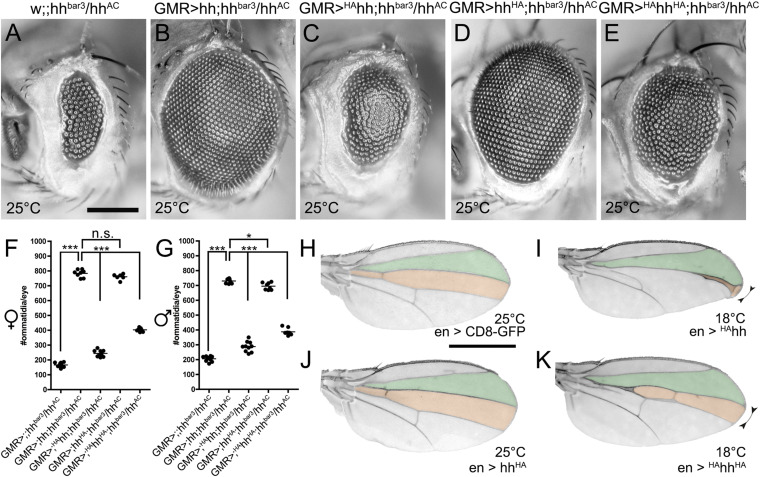
FIGURE 4.
N- and C-terminal insertion of HA tags affect Hh biofunction to different degrees. (A–E) Eye phenotypes in (A) hhbar3/hhAC flies that express (B) untagged hh, (C) N-terminally HA tagged HAhh, (D) C-terminally HA tagged hhHA, or (E) N- and C-terminally tagged HAhhHA, all under GMR-control at 25°C. Scale bar: 100 μm. (F,G) Quantification of female or male fly eyes shown in (A–E). Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple-comparison test. ***P < 0.001, *P < 0.05, P > 0.05 was considered as not significant (n.s.) (H–K) Representative wing patterning in flies expressing (H) CD8-GFP as a negative (inactive) transgene control, (I) N-terminally HA tagged HAhh that suppresses the activity of endogenous Hh expressed in the same compartment, (J) C-terminally HA tagged hhHA, or (K) dually HA tagged HAhhHA, all under En-Gal4 control. Because N-terminal HA tagging resulted in pharate lethality at 25°C, the experiment was conducted at 18°C. Scale bar: 1 mm.