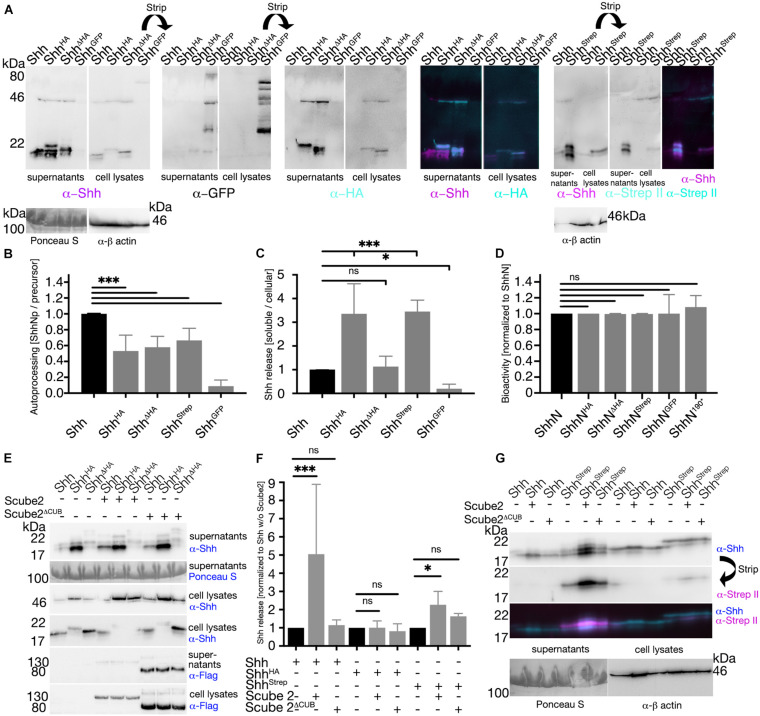
FIGURE 7.
C-terminal tags impair ShhNC autocatalytic cholesteroylation and regulated Shh release. (A) Representative Western blots of C-terminally modified Shh variants. Solubilized Shh (supernatant) and cellular Shh (cell lysates) were blotted and stained with antibodies directed against Shh or its C-terminal tags. (B) Quantification of autocatalytic cholesteroylation efficiencies. Ratios of processed cellular Shh relative to precursors were determined and processing of the untagged protein was set to 1 (black bar). (C) Quantification of Shh release. Ratios of soluble (supernatant) Shh relative to cellular (cell lysate) Shh were determined and untagged protein release was set to 1 (black bar). Mean values ± SD are shown. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test. ns: not significant *P < 0.05 ***P < 0.001. (D) Bioactivity of Shh and its C-terminally modified variants. Non-cholesterol modified but C-terminally tagged Shh was expressed in Bosc23 cells and subsequently induced osteoblast differentiation of C3H10 T1/2 reporter cells. C-terminal protein tags did not interfere with Ptc receptor binding. (E,G) Representative Western blots of Shh or its variants with or without Scube2 and inactive Scube2ΔCUB. (F) Quantification of (E,G). Mean values ± SD are shown in all graphs. Statistical significance was determined by one-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple-comparison test. ns: not significant, *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001.