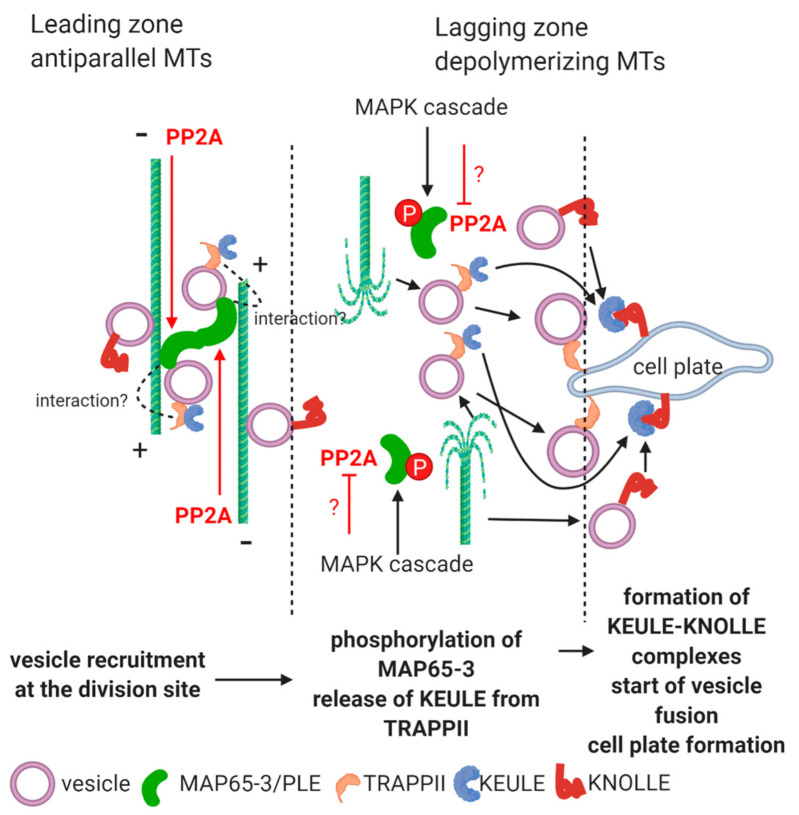
Figure 1.
Confirmed and proposed roles of PP2A in vesicle traffic at the formation of the cell plate. For simplifying reasons, the kinesin motors that bind and deliver vesicles along phragmoplast MTs are not shown here. In the leading zone of phragmoplast, MAPK cascade-mediated phosphorylation of MAP65-3/PLE is not functional, while presumably a PP2A complex is dephosphorylating this MAP. As a consequence, it can cross-link antiparallel MTs, while it binds TRAPPII-containing vesicles that in turn, assure the KEULE-MT connection. MAP65-3 is phosphorylated via a MAPK cascade at the lagging zone, while PP2A is possibly inhibited. Thus, MAP65-3 detaches from MTs that will be destabilized as a consequence. This will release TRAPPII/KEULE containing vesicles to the site of cell plate formation and KEULE can interact with KNOLLE, allowing the t-SNARE function of the latter. This triggers vesicle fusion. Confirmed or possible pathways involving PP2A are shown in red. Question marks indicate probable, yet hypothetical events. Figure was constructed with the aid of BioRender.com.