Figure 1: Metabolic pathways and signaling in cancer.
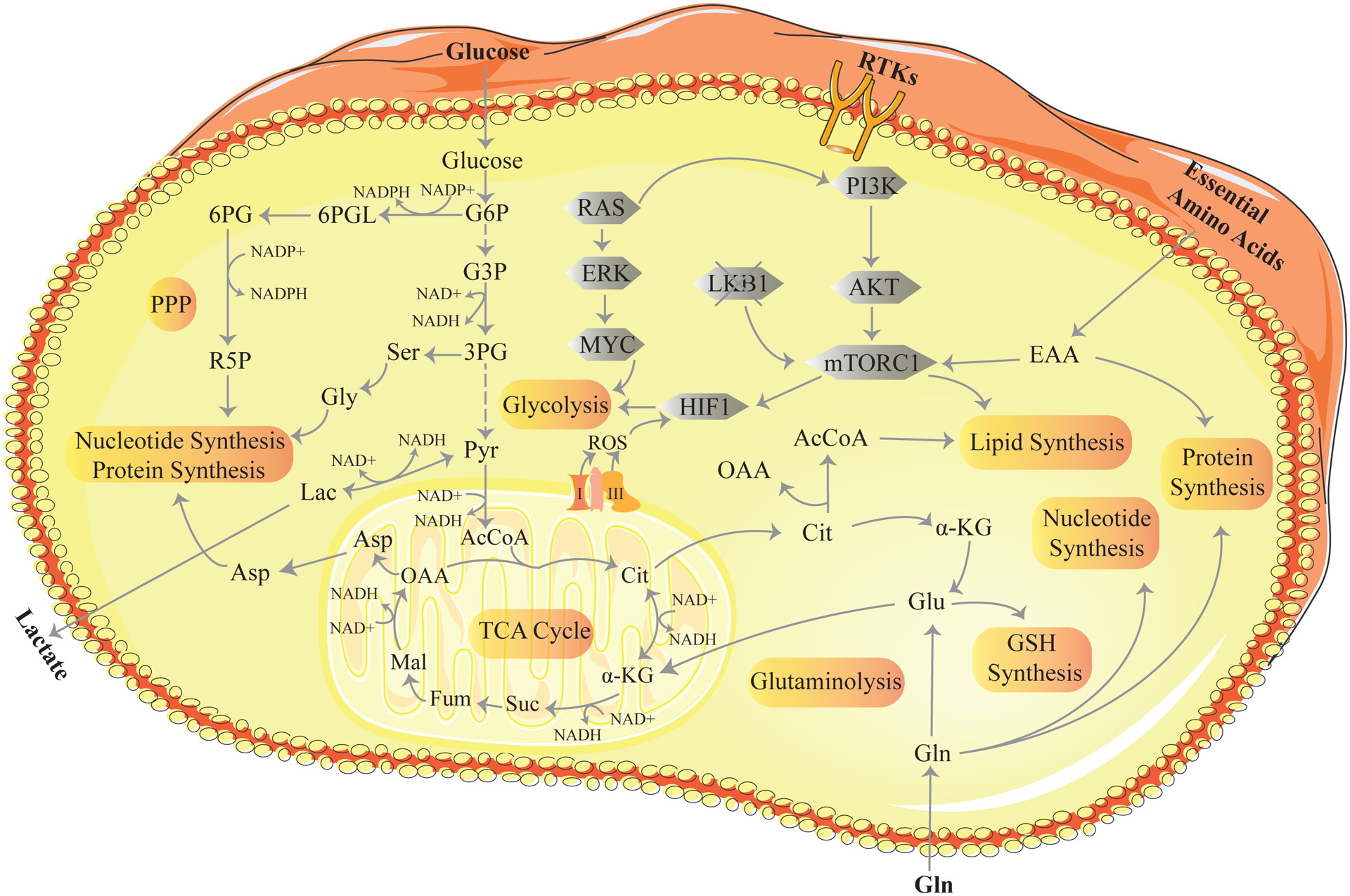
The key metabolic processes are highlighted in orange. Glycolysis is a 10-step process that converts glucose to pyruvate releasing energy in the form of ATP and NADH. The pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) generates NADPH used for the biosynthesis of fatty acids, cholesterol and reduced glutathione. In addition, the PPP generates ribose-5-phosphate required for the synthesis of purines, pyrimidines, nucleotides and nucleic acids. In the mitochondria, glycolytic-derived pyruvate is fed into the tricarboxylic acid (TCA) cycle. TCA cycle dehydrogenases consume NAD+ to produce NADH. Each turn in the cycle forms three NADH molecules. Nucleotide synthesis provides molecules that make up the nucleic acids RNA and DNA. Lipid synthesis is the synthesis of fatty acids from acetyl Co-A and malonyl-CoA precursors via fatty acid synthases. Glutaminolysis is a series of biochemical reactions that converts glutamine to α-ketoglutarate. This takes place outside and inside the mitochondria. GSH (glutathione) synthesis is the synthesis of GSH from glutamate, cysteine, and glycine. The grey shapes represent the signaling events that influence cancer metabolism. RAS activates the transcriptional program for metabolic enzymes through the activation of the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway leading to upregulation of the MYC transcription factor. MYC promotes metabolic phenotypes through transcriptional regulation of key metabolic genes. Receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) activate PI3K/AKT/mTORC1 signaling. Through a series of downstream effectors mTORC1 promotes anabolic growth by converting available nutrients for lipid, nucleotide and protein synthesis. Mutant LKB1 results in the hyper-activation of mTORC1 signaling and elevated HIF signaling and glycolysis. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) are generated by the electron transport chain (complex I and III) on the mitochondria membrane and activate HIF signaling. 6PG, 6-P-gluconate; R5P, Ribose-5-phosphate; Ser, Serine; Gly, Glycine; G6PL, glucose-6-phosphogluconolactone; G6P, glucose-6-phosphate; G3P, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate; 3PG, 3-phosphoglycerate; Pyr, pyruvate; Lac, Lactate; Cit, citrate; α-KG, α-ketoglutarate; Suc, succinate; Fum, fumarate; Mal, malate; Asp, aspartate; OAA, oxaloacetate; Gln, glutamine; Glu, glutamate; EAA, essential amino acids.
