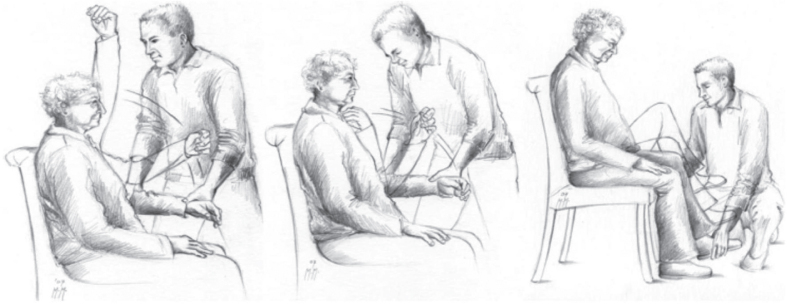
Fig. 3.
The PAI procedure: The examiner starts with a slow movement of the limb, after which the movement is accelerated. A construct of five criteria allows a categorical diagnosis of paratonia, i.e., paratonia can only be diagnosed when all five criteria are present; 1) an involuntary variable resistance; 2) a degree of resistance that varies depending on the speed of the movement (e.g., a low resistance to slow movements and a high resistance to fast movement; 3) resistance to passive movement can be felt in any direction (no distinct pattern); 4) no clasp-knife phenomenon; and 5) resistance is present in 2 movement directions in 1 limb or in 2 different limbs. With permission from Cambridge University Press reprinted from; Diagnosing paratonia in the demented elderly: reliability and validity of the Paratonia Assessment Instrument (PAI) [42].