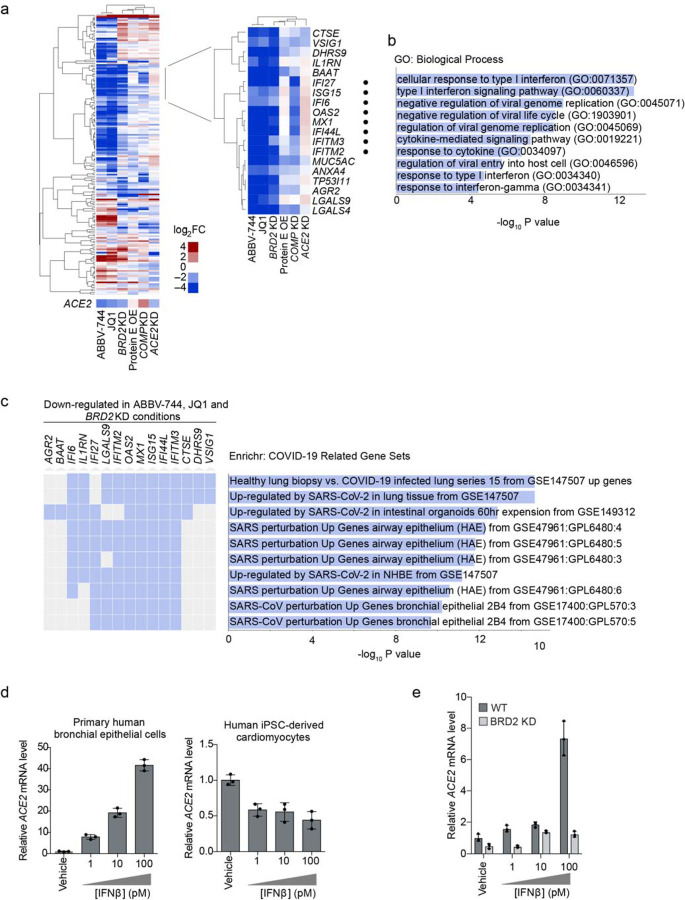
Figure 4: BRD2 controls genes induced by interferon and SARS-CoV-2 infection.
a, Differentially expressed genes from RNA sequencing of Calu-3 cells under different treatment conditions compared to control cells: 72-hour treatment with 10 μM JQ1 or 10 μM ABBV-744, BRD2 knockdown (KD), SARS-CoV-2 protein E overexpression (OE), COMP KO, ACE2 KD. Heatmap showing log2-fold change (log2FC) for each condition relative to untreated controls (columns) for genes that are among top 50 differentially expressed genes (ranked by P values) in at least one of the conditions (rows). ACE2 was not among these genes and is shown as a separate row. Insert, a cluster of genes that are down-regulated in both BRD2 inhibition by JQ1 and ABBV-744 and BRD2 knockdown. Among these, genes associated with the GO term “Cellular Response to Type I interferon” are marked by black dots. b, Significantly enriched (FDR < 0.05) GO biological process terms for the genes shown in the inset in (a). c, Enrichment analysis for genes in the inset in (a) reveals COVID-19 related gene sets. Genes that appear in a gene set are marked in blue. d, Primary human bronchial epithelial cells (left) and human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes (right) were treated with the indicated concentrations of interferon-beta (IFNβ), and transcript levels of ACE2 relative to ACTB (for Calu-3 and NHBE) or 18S rRNA (cardiomyocytes) were quantified at 72 hours post-treatment by qPCR. Average and standard deviation of 3 technical replicates are shown for each condition. e, WT (dark grey) or BRD2 knockdown (light grey) Calu-3 cells were treated with the indicated concentrations of interferon-beta (IFNβ), and transcript levels of ACE2 relative to ACTB were quantified at 72 hours post-treatment by qPCR. Average and standard deviation of 3 technical replicates are shown for each condition.