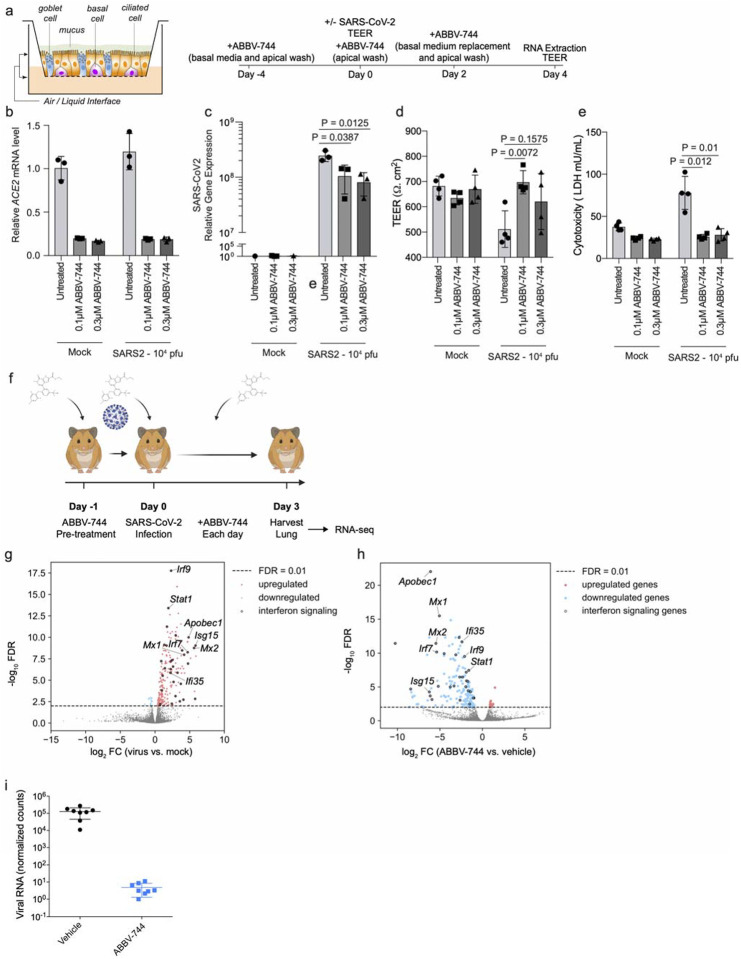
Figure 6: Brd2 inhibitors prevent cytotoxicity and reduce SARS-CoV-2 infection in human primary nasal epithelia and inhibit SARS-CoV-2 infection in Syrian Hamsters.
a, Experimental design for experiment in reconstructed human nasal epithelia. b, ACE2 transcript levels relative to the average of GAPDH, TFRC, RPL13, and ACTB as a function of ABBV-744 concentration and/or SARS-CoV-2 infection (right). c, intracellular SARS-CoV-2 gene expression (N) relative to the average of GAPDH, TFRC, RPL13, and ACTB as a function of ABBV-744 concentration and/or SARS-CoV-2 infection (right). P-value was determined using Student’s unpaired two tailed t-test. d, Transepithelial electrical resistance (TEER), a measure of epithelial barrier integrity, evaluated as a function of ABBV-744 concentration and/or SARS-CoV-2 infection. P-value was determined using Student’s unpaired two tailed t-test. e, Cytotoxicity, as measured by lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release, evaluated as a function of ABBV-744 concentration and/or SARS-CoV-2 infection. P-value was determined using Student’s unpaired two tailed t-test. Experiments a-d are done in at least biological triplicates with error bars representing the standard deviation. f, Experimental design for Syrian hamster experiments. g, Volcano plot showing differentially expressed genes for Syrian hamsters lungs infected or not infected with SARS-CoV-2. A subset of ISGs for which BRD2 peaks were identified by CUT&RUN are labeled. h, Volcano plot showing differentially expressed genes for Syrian hamsters lungs infected with SARS-CoV-2 and treated with vehicle or ABBV-744 at 100nM. A subset of ISGs for which BRD2 peaks were identified by CUT&RUN are labeled. i, Normalized viral RNA counts for Syrian hamsters infected with SARS-CoV-2 and treated with vehicle or ABBV-744 at 100 nM.