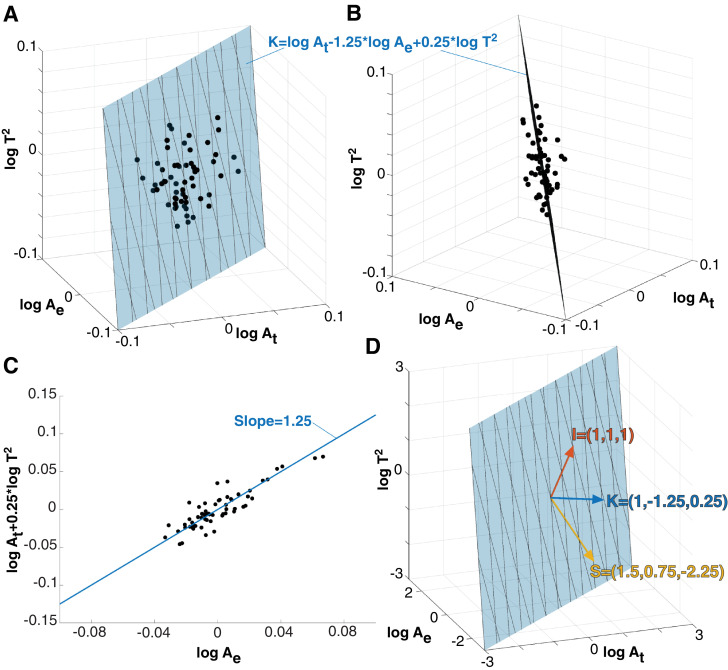
Fig. 2.
Universal scaling law describes the covariance of the raw morphological measures. (A) Three raw morphoplogy measures span a 3D space, where each cortex is a data point (black dots). Here we used the control group in the TLE dataset as an example for the purpose of illustration. The data points align with the plane described by the universal scaling law (blue plane). (B) different viewing angle of the same data shown in (A). (C) Projection of data into a 2D space, which was previously used to visualise the scaling law. The blue line now represents the projected plane from (A) and (B). (D) 3D view of scaling law plane and viewing angle as in (A). The normal vector of the scaling law plane (K) is shown as a blue vector. Two perpendicular vectors (S and I) can be defined, and together they span the 3D space. All morphological variables are logscaled and age corrected in this figure. Cortical thickness is presented as thickness squared so that the 3D space has units of area in all dimensions.