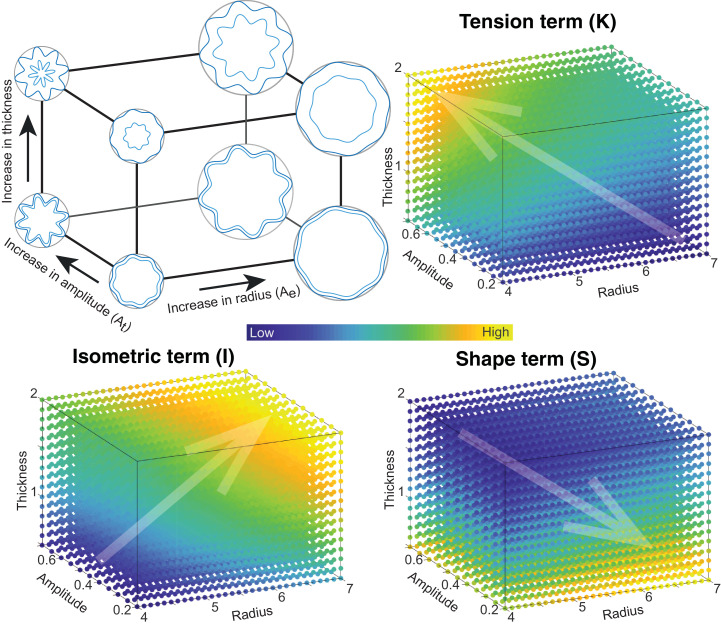
Fig. 3.
Schematic to provide intuition for the three projection terms K, S, and I Simulations of basic folded ribbons as sinusoidal oscillations on a circle. In this shape we can change the overall radius of the encapsulating circle (), the thickness () encapsulated by the outer and inner oscillations (dark and light blue), and the amplitude of the oscillations, which dictate the total length of the oscillation (). By scanning the radius, thickness, and oscillation amplitude in a 3D space, we can calculate the corresponding value for the and term at different points in this space (colour map). Transparent arrows point in the directions of change of and . Through visualising the changes in and in this 3D space, we provide an intuition for how the three terms relate to parameters in a simple folded structure.