Figure 1.
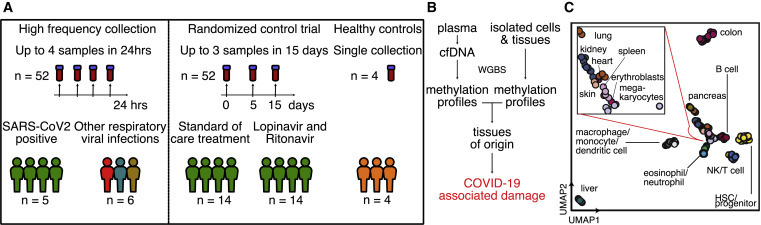
Study design
(A) Two independent cohorts were used in our study. First, a high-frequency collection cohort with 5 SARS-CoV-2 patients (n = 52 samples) and 6 SARS-CoV-2-negative, RNA virus-positive patients (n = 6 samples). Second, a randomized controlled trial of 28 SARS-CoV-2 patients with plasma at serial time points (n = 52 samples). Four healthy individuals volunteered plasma for cell-free DNA analysis.
(B) Experimental workflow. cfDNA is extracted from plasma, and whole-genome bisulfite sequencing is performed. In parallel, methylation profiles of cell and tissue genomes are obtained from publicly available databases. cfDNA methylation profiles are compared to those of cell and tissue references to infer relative contributions of tissues to the cfDNA mixtures.
(C) UMAP of differentially methylated regions for isolated cell and tissue types used as a reference.
