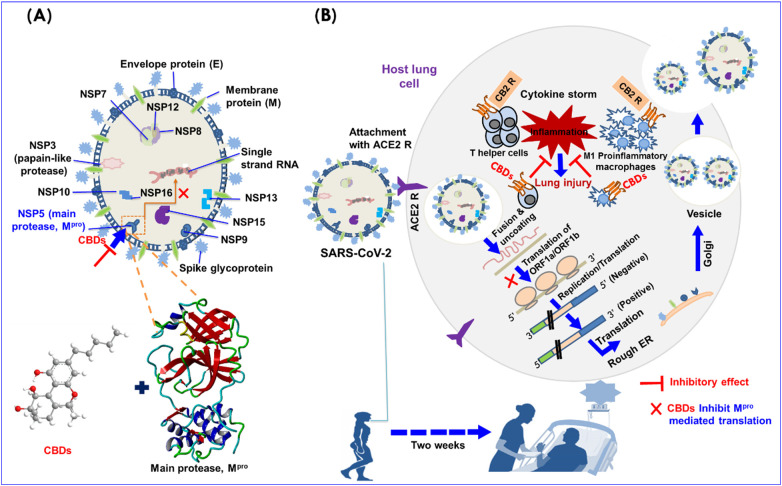
Fig. 6.
A. A plausible mechanism of CBDs as may act dual-acting to inhibit SARS-CoV-2: structure features of SARS-CoV-2 and its main SARS-CoV-2 Mpro binding pocket, B. SARS-CoV-2 life cycle in host lung cells is initiated by binding between viral spike glycoprotein and ACE2 cellular receptor. Spike glycoprotein facilitates viral envelope/cell fusion through the endosomal pathways, consequently, release RNA of SARS-CoV-2 and translate the RNA genome of viral by viral polyproteins replicase of 1ab and pp1a and their subsequent cleavage by the viral proteinases into small products. A sequence of subgenomic mRNAs is produced by SARS-CoV-2 Mpro, which are next translated into similar viral proteins. Further, genome RNA and viral proteins accumulate into virions in the ER and Golgi, and SARS-CoV-2 is transported in vesicles to the extracellular compartment. During this process, T-helper cells and M1 pro-inflammatory macrophages secrete interleukins and induce inflammation inside lung cells.