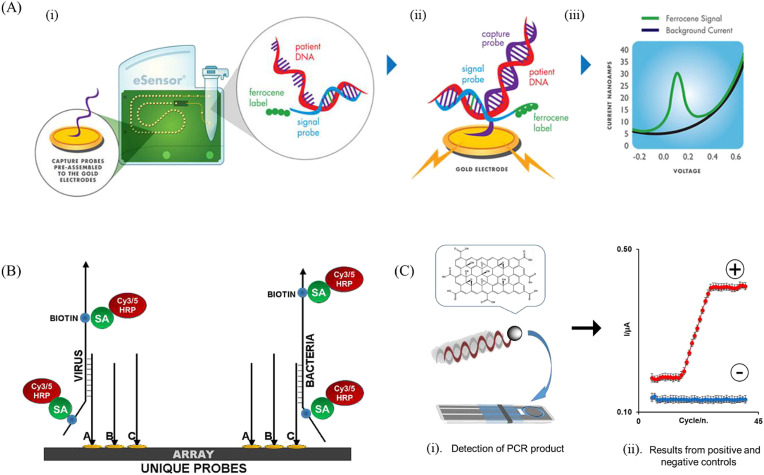
Fig. 4.
Electrochemical detection of PCR amplification products: (A) Experimental principle of Genmark's eSensor® technology (i) hybridization of signal probe to the target DNA, (ii) reaction of target DNA/signal probe with the captured probe in the cartridge's microfluidic chamber, (iii) collection of the voltammetric response from the target DNA [53]. Adapted with permission from Ref. [53]; (B) Schematic diagram on the microarray for detection of target viral and bacterial analytes. Single-stranded biotinylated target sequence is first hybridized to the immobilized complementary probes (A, B and C) before labelling with streptavidin (SA)-horseradish peroxidase (HRP) to enable electrochemical detection [54]. Adapted with permission from Ref. [54]; (C) Electrochemical PCR scheme using graphene oxide nanoparticles as labels for DNA primers: (i) Electrochemical detection on miniaturized electrode; (ii) nanographene oxide reduction current vs PCR cycle number for positive (red) and negative control (blue) [26]. Reproduced with permission from Ref. [26].