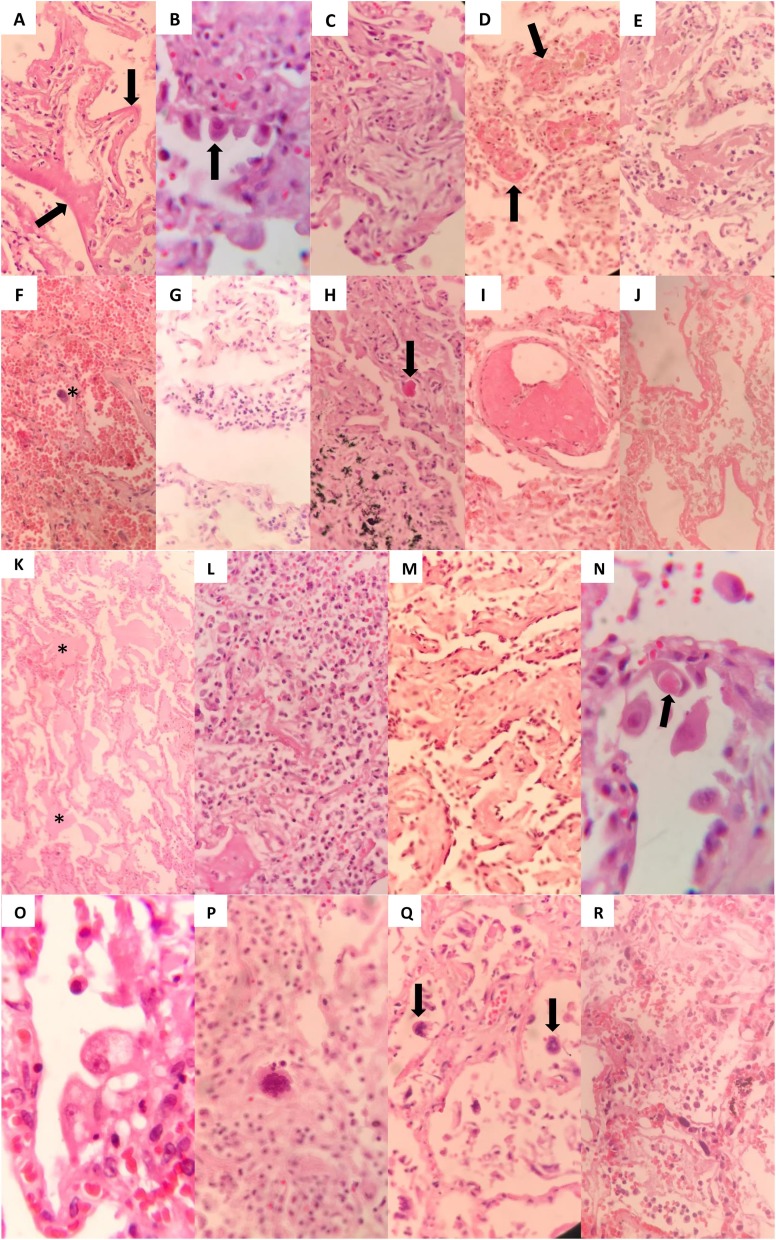
Fig. 3.
Histopathologic findings in lung biopsy specimens.
A. Exudative phase of diffuse alveolar damage with prominent hyaline membrane formation (black arrows), B. Proliferative phase of diffuse alveolar damage with prominent type 2 pneumocyte hyperplasia (black arrow), C. Intraalveolar organization (late proliferative to early repair phase), D. Intra-alveolar fibrin balls (black arrows) with focal organization, E. Acute fibrinous and organizing pneumonia pattern, F. Diffuse obscuring alveolar hemorrhage; note the included binucleated cell with hyperchromatic nucleus (asterisk), G. Interstitial and intracapillary neutrophil accumulation, H. Microvascular thrombosis as a component of microangiopathy (black arrow), I. Organized thrombus in a small pulmonary vessel, J. Parenchymal infarction; note the included hyaline membranes. K. Alveolar edema and capillary congestion in early exudative phase (asterisks), L. Suppurative bronchopneumonic changes; note alveolar spaces filled with neutrophils, M. Areas of interstitial thickening by collagenous fibrosis, N. Alveolar lining cell with intracytoplasmic inclusion of unknown nature (black arrow), O. Alveolar lining cell with cytoplasmic vacuolation and a small eosinophilic inclusion, P. Syncytial cells with multiple irregular to overlapping nuclei, Q. Cells with smudged hyperchromatic nuclei (black arrows), R. Increased intracapillary megakaryocytes.