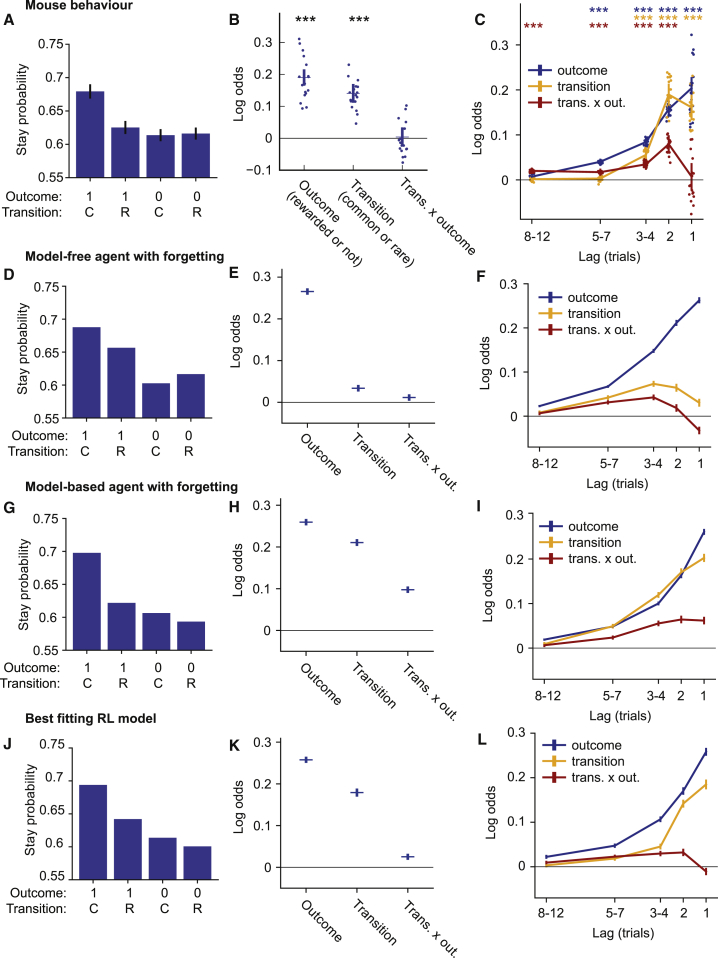
Figure 2.
Stay Probability and Logistic Regression Analyses
(A–C) Mouse behavior. (A) Stay probability analysis showing the fraction of trials the subject repeated the same choice following each combination of trial outcome (rewarded [1] or not [0]) and transition (common [C] or rare [R]). Error bars show cross-subject SEM. (B) Logistic regression model fit predicting choice as a function of the previous trial’s events. Predictor loadings plotted are outcome (repeat choices following rewards), transition (repeat choices following common transitions), and transition-outcome interaction (repeat choices following rewarded common transition trials and non-rewarded rare transition trials). Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals on the population mean, dots indicate maximum a posteriori (MAP) subject fits. (C) Lagged logistic regression model predicting choice as a function of events over the previous 12 trials. Predictors are as in (B).
(D–F) As (A)–(C) but for data simulated from a model-free RL agent with forgetting and multi-trial perseveration.
(G–I) As (A)–(C) but for data simulated from a model-based RL agent with forgetting and multi-trial perseveration.
(J–L) As (A)–(C) but for data simulated from the best fitting RL model found by model comparison.
Parameters for all RL model simulations were obtained by fits of the RL models to the mouse behavioral data.