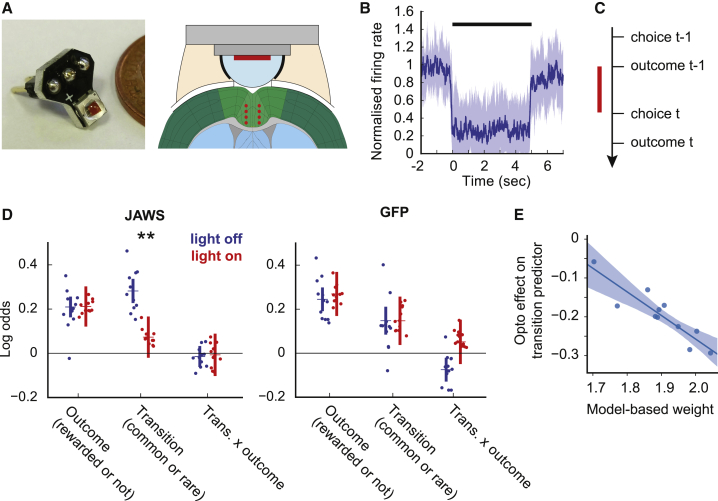
Figure 6.
Optogenetic Inhibition of ACC in the Two-Step Task
(A) LED implant (left) and diagram showing implant mounted on head (right); red dots on diagram indicate location of virus injections.
(B) Normalized firing rate for significantly inhibited cells over 5 s illumination; dark blue line, median; shaded area, 25th to 75th percentiles.
(C) Timing of stimulation relative to trial events. Stimulation was delivered from trial outcome to subsequent choice.
(D) Logistic regression analysis of ACC inhibition data showing loadings for the outcome, transition, and transition-outcome interaction predictors for choices made on stimulated (red) and non-stimulated (blue) trials. ∗∗Bonferroni-corrected p < 0.01 between stimulated and non-stimulated trials. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals on the population mean, dots indicate maximum a posteriori (MAP) subject fits.
(E) Correlation across subjects between the strength of model-based influence on choice (assessed using the RL model’s model-based weight parameter, Gmb) and the effect of optogenetic inhibition on the logistic regression model’s transition predictor.