Figure 2.
eIF2(αP) and ISRIB Associate with Different Conformations of eIF2B
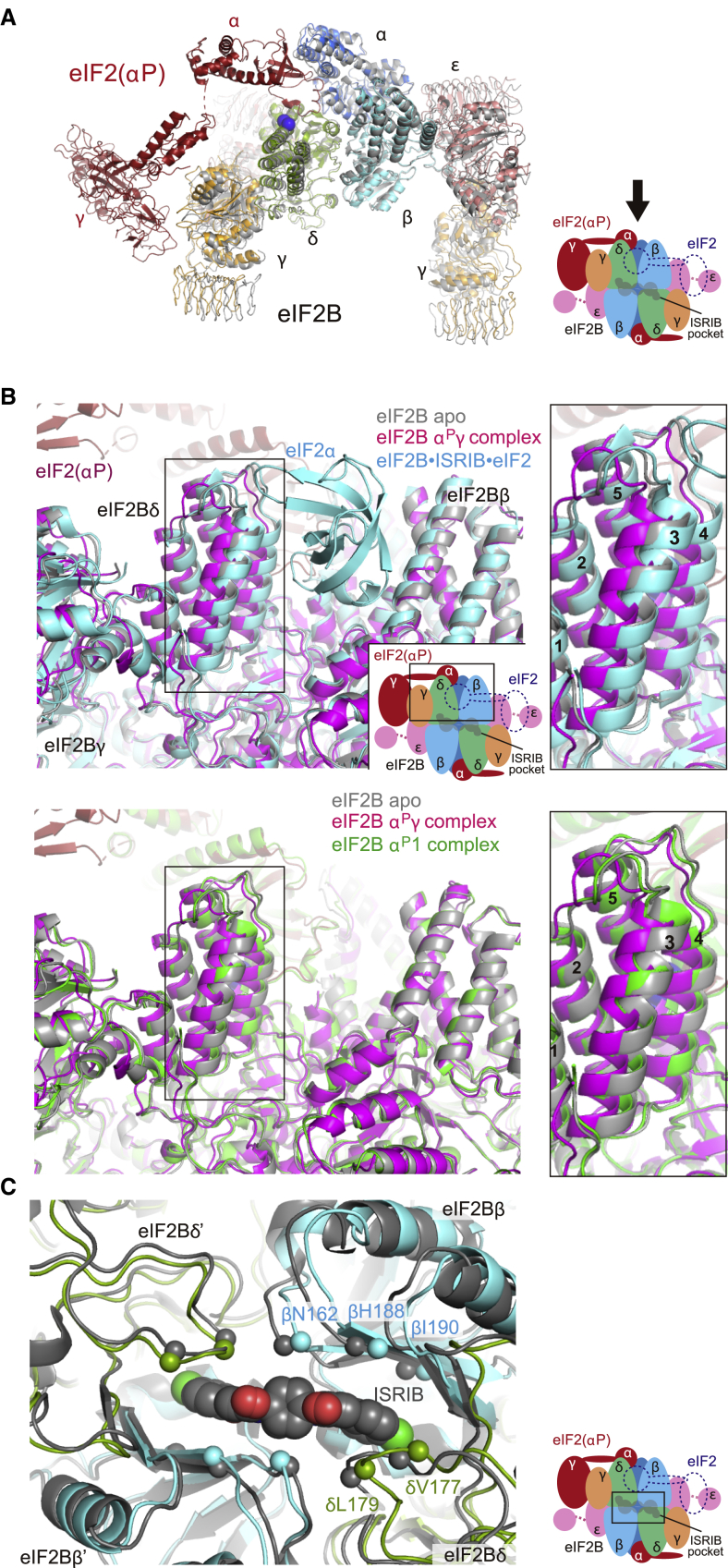
(A) Overlay of the eIF2B apo structure (gray) and eIF2B in complex with two eIF2(αP) trimers (the αPγ complex; color-coded as in the adjacent cartoon). The blue spheres show the position of the Cα atoms of eIF2BδE310 and δL314.
(B) Different arrangements of the eIF2B pocket that accommodates the eIF2α-NTD: unphosphorylated in the catalytically productive conformation, and phosphorylated in complexes containing one (αP1) or two (αPγ) bound eIF2(αP) trimers. Upper panels: an overlay of the productive eIF2B⋅ISRIB⋅eIF2 complex (cyan, PDB: 6O81), the eIF2B apo structure (gray), and the αPγ complex (magenta). For clarity, only the unphosphorylated eIF2α-NTD of the eIF2B⋅ISRIB⋅eIF2 complex is shown. Lower panels: similar alignment of the apo structure, the αPγ structure, and the αP1 structure (green). Right panels: close-up views showing the displacements of helix δ-α3 between the different complexes.
(C) Deformation of the ISRIB-binding pocket in eIF2B with two bound eIF2(αP) trimers (the αPγ complex). The eIF2B⋅ISRIB complex structure (PDB: 6CAJ) is shown in gray and the αPγ complex in color-coded representation (as in the adjacent cartoon). Key residues known to affect the binding or action of ISRIB are highlighted as spheres.
Structures are aligned by the four C-terminal domains of the β- and δ-subunits of eIF2B for (A) and (B), and by the Cα atoms surrounding (within 10 Å) the ISRIB molecule in the eIF2B⋅ISRIB structure for (C).
See also Figures S1 and S2.