Figure 2: Increased frequency of IPs integrated in centromeric satellite DNA in ECs.
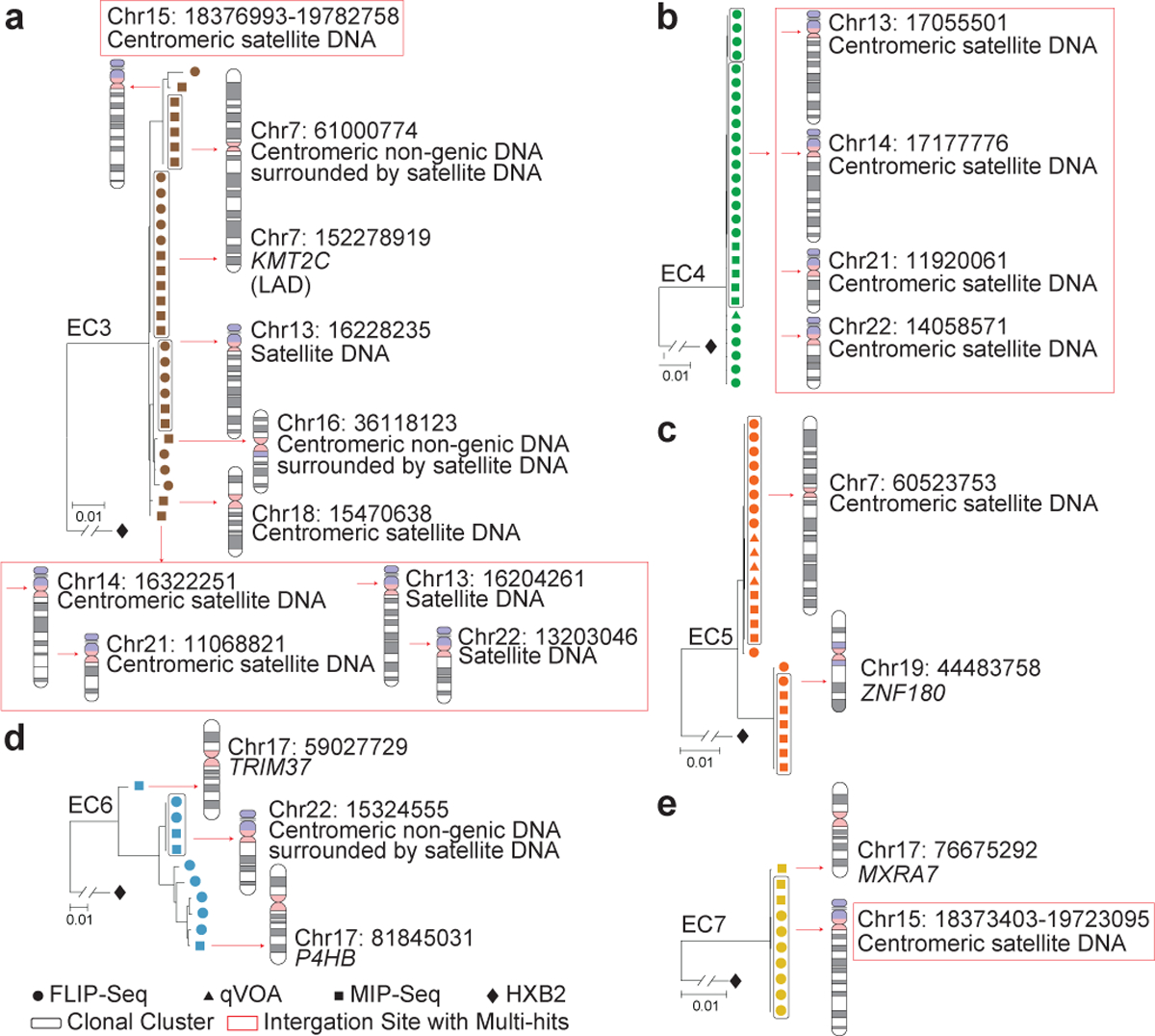
(a-e): Data indicate linear maximum-likelihood phylogenetic trees for IPs from five ECs. Coordinates and relative positioning of IS are depicted; genes harboring IS are italicized. Clonal IPs, defined by identical proviral sequences and identical corresponding IS, are highlighted in curved black boxes. Red boxes reflect multi-hit IS that cannot be definitively mapped to one particular genomic location due to positioning in repetitive centromeric satellite DNA present in multiple regions of the human genome. LAD, lamina associated domain.
