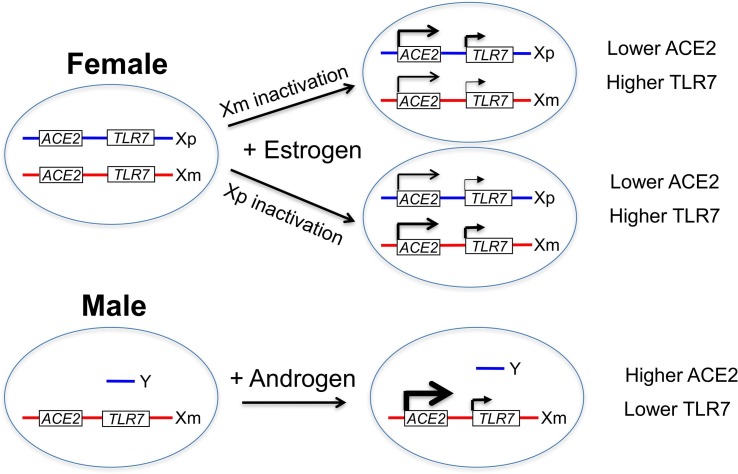
Fig. 1.
Regulation of ACE2 and TLR7 gene expression on X chromosome. Both ACE2 and some immune regulatory genes such as TLR7 are located on X chromosome. The ACE2 gene was reported to largely escape X chromosome inactivation in most tissues in females. Thus, the ACE2 gene is expressed at relatively high level (more than half) from its allele located on the randomly inactivated paternal X (Xp) or maternal X (Xm) chromosome, compared with its counterpart on the active X chromosome. The ACE2 gene is only expressed from the active maternal X (Xm) chromosome in the males since it is not present on Y chromosome. Expression of the ACE2 gene is also regulated by estrogen in the females and androgen in the males. It may be regulated by other sex hormones too. As a result of sexual hormone regulation, the ACE2 protein is present at higher levels in most cells in the males compared with the females. Thus, expression of ACE2 is dependent on sex hormones whereas its expression level may not be regulated by X inactivation in females. By contrast, the TLR7 gene is subject to random X chromosome inactivation in females so that it is only expressed at much lower level (much less than half) from its allele located on the randomly inactivated X chromosome, compared with the other allele on the active X chromosome. However, its expression may not be regulated by sex hormones. Therefore, it has higher expression level in the females due to extra expression of the TLR7 gene from the inactivated X chromosome, compared with the males.