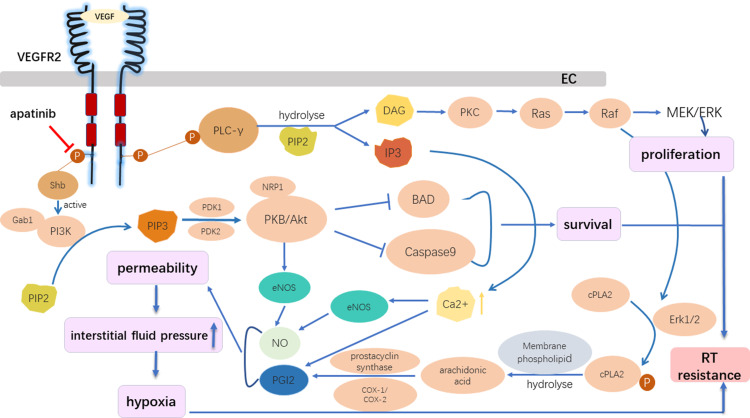
Figure 3.
The role of the VEGFR2 inhibitor in the reversal of radioresistance. Apatinib, which acts on the intracellular segment of VEGFR2, inhibited downstream signal activation despite the binding between VEGF with VEGFR2 in vascular endothelial cells, preventing the activation of the following pathways: the Ras/Raf/MEK/ERK pathway, which promotes EC proliferation; and the PI3K/AKT pathway, which inhibits EC apoptosis and promotes EC survival. The activation of VEGF/VEGFR2 could increase the intracellular calcium concentration, activating endothelial nitric oxide synthase, and promoting the production of nitric oxide and prostacyclin. Thus, vascular cell permeability greatly increased, followed by an increase in the interstitial fluid pressure, which is further aggravated by hypoxia. The VEGFR2 inhibitor overcame radiation resistance by inhibiting the proliferation and survival of ECs and reducing hypoxia.
Abbreviations: BAD, Bcl-2 associated death promoter; COX-1/2, cyclooxygenases; DAG, sn-1,2-diacylglycerol; EC, endothelial cell; ERK ½, extracellular regulated kinases 1 and 2; Gab1, Grb2-associated binder-1; IP3, inositol (1,4,5)-trisphosphate; eNOS, endothelial nitric oxide synthase; NO, nitric oxide; PDK1/2, phosphoinositide-dependent kinases 1 and 2; PGI2, prostacyclin; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; PIP2, phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate; PIP3, phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-trisphosphate; PKB, protein kinase B; PKC, protein kinase C; cPLA2, cytosolic phospholipase A2; PLC-γ, phospholipase C-γ; Shb, Src Homology 2 domain-containing adapter protein B.