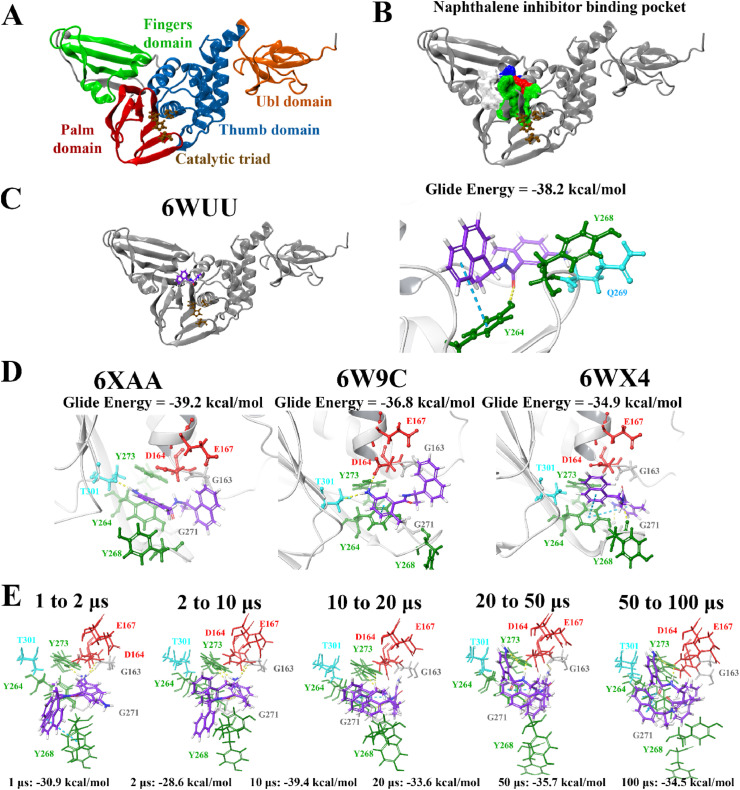
Fig. 1.
Binding of the noncovalent inhibitor GRL-0617 to various forms of PLpro. The SARS-CoV-2 PLpro contains several domains highlighted in A), and catalytic triad residues C111, H272, and D286 are shown. PrankWeb analysis identified the naphthalene inhibitor binding pocket as a potential binding site (B). The known inhibitor GRL-0617 was docked to the binding pocket in various structures of the PLpro protein (C, D), as well as along time points of a molecular dynamics simulation trajectory in E). Residue interactions are shown as dashed lines, including hydrogen bonds (yellow), salt bridges (magenta), π−π interactions (cyan), and π−cation interactions (green). Amino acid residues are coloured according to their properties, namely hydrophobic residues (green), polar uncharged residues (cyan), negatively charged residues (red), and glycine residues (grey). (For interpretation of the references to colour in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the Web version of this article.)