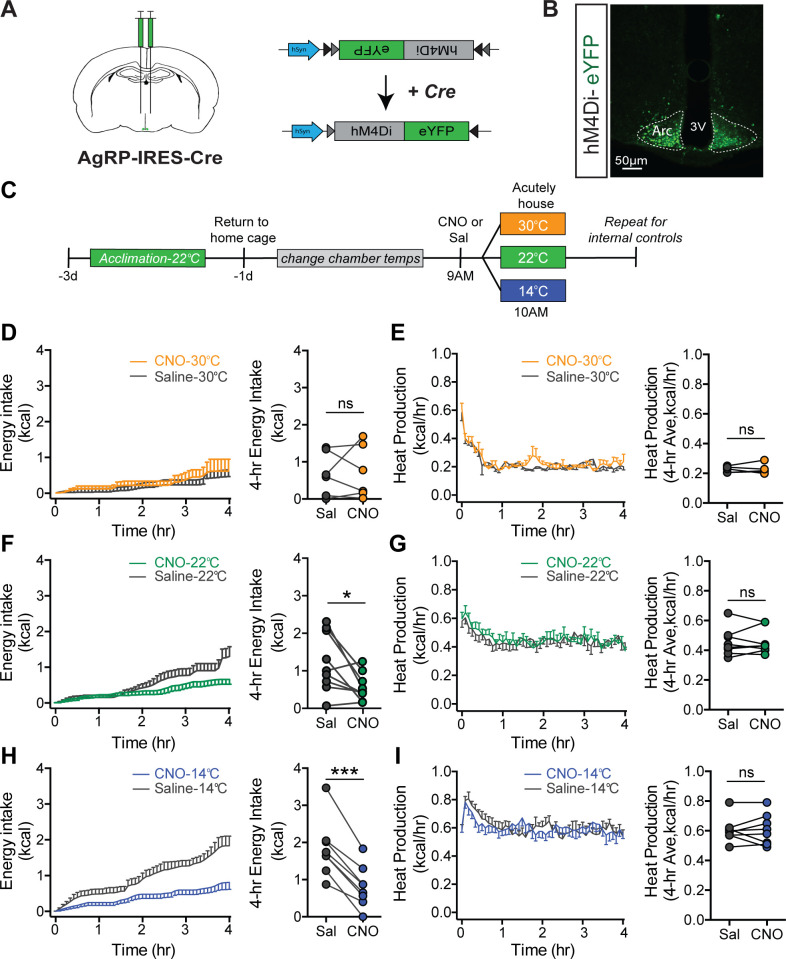
Figure 5. Cold-induced hyperphagia, but not thermogenesis, requires activation of agouti-related peptide (AgRP) neurons.
(A) Schematic depicting strategy for bilateral microinjection of the Cre-dependent inhibitory DREADD (hM4Di) virus into the arcuate nucleus (ARC) of AgRP-IRES-Cre mice. (B) Detection of bilateral hM4Di-eYFP in transduced AgRP neurons in the ARC. (C) Adult male hM4Di-eYFP AgRP-IRES-Cre mice were acclimated to temperature-controlled chambers set to 22°C. Animals were returned to their home cages and chamber temperatures were adjusted overnight. In the morning, animals were dosed i.p. with either CNO or saline 1 hr prior to being acutely housed at either mild cold (14°C), room temperature (22°C), or thermoneutrality (30°C) in a randomized, crossover manner. (D, F, and H) 4 hr time-series and mean values for energy intake, and (E, G, and I) 4 hr time-series and mean values of heat production in hM4Di-eYFP AgRP-IRES-Cre mice that were housed at either 30°C, 22°C, or 14°C after receiving an i.p. injection of either saline or CNO n = 6–8 per group, mean ± SEM. RM-ANOVA and Student’s t-test, ***p<0.001, *p<0.05 vs. saline.
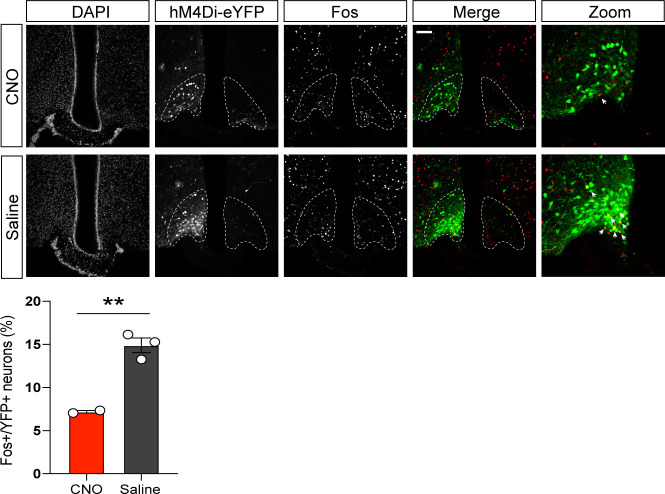
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Inhibition of cold-induced Fos in hM4Di-expressing agouti-related peptide (AgRP) neuron.
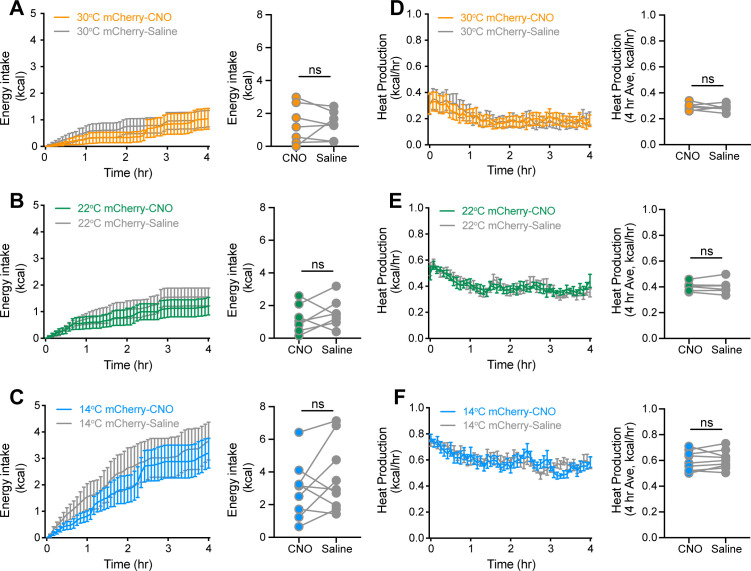
Figure 5—figure supplement 2. CNO controls associated with inhibition of agouti-related peptide (AgRP) neurons during acute exposure to three ambient temperatures.
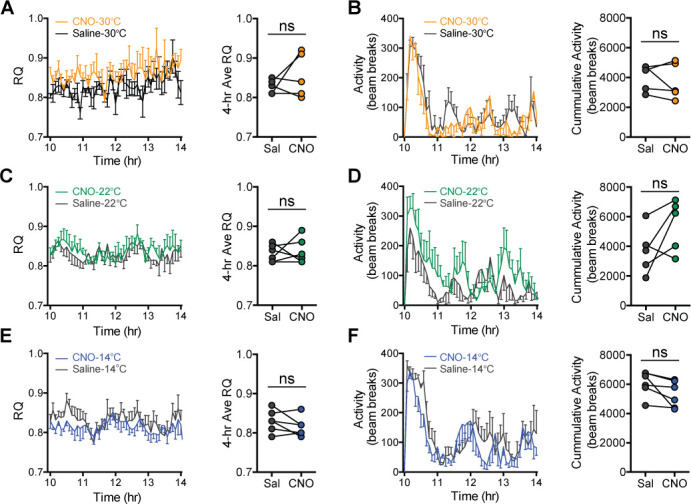
Figure 5—figure supplement 3. Respiratory quotient (RQ) and ambulatory activity after agouti-related peptide (AgRP) neuron inhibition at three ambient temperatures.