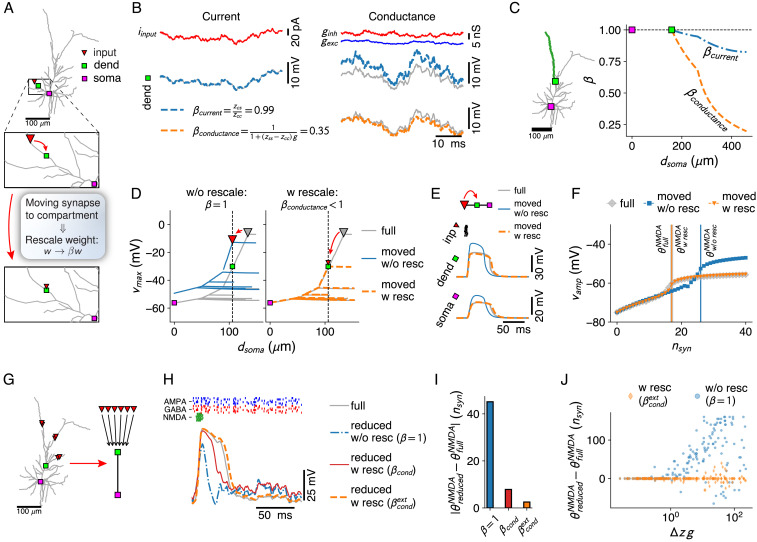
Figure 4. Simplification of afferent spatial connectivity motifs.
(A) Removal of a branch with a synapse (red triangle) is considered possible if the correct voltages at the compartment sites (here, dendritic – green square and somatic – purple square) can be obtained by shifting the synapse to the compartment site and rescaling its weight with a fixed factor for the all input conditions under consideration. (B) Comparison between weight-rescale factors for current-based (left) and conductance-based (right) input. Voltage trace for dendritic compartment without rescaling (gray) and with the current-based scale factor compensating for attenuation (blue). Bottom right panel shows voltage trace with conductance-based scale factor . (C) Current- and conductance-based scale factors in the green dendritic branch, for a shift of a synapse at a given distance from the soma to the dendritic compartment site (green square). (D) Spatial peak voltage without (left, blue) and with (right, orange) application of . (E) For a cluster of AMPA+NMDA synapses in isolation, scale factors for physiological constants can be obtained (see Materials and methods — Synaptic weight-rescale factors) that reproduce the correct voltage waveform. Colors as in D. (F) Maximal amplitude of NMDA-spike waveform upon activation of increasing numbers of synapses – NMDA-spike thresholds indicated with vertical lines. Colors as in D. (G–H) Removing a whole subtree and shifting multiple synapses (red triangles) to the next proximal compartment site (green square). NMDA-spike generation (gray voltage trace) at the compartment site through burst inputs to local AMPA+NMDA synapses (green inputs), with AMPA (blue) and GABA (red) background inputs spread throughout the subtree. Reductions shown without rescaling (blue, dash-dotted), with the analytical single-site rescaling rule (red, full) and the numerical multi-site rule (orange, dashed). (I) Error in NMDA-spike threshold for the three cases in H. (J) Dependence of the error in NMDA-spike threshold on the factor , with the average input resistance difference between synapse sites and the compartment and the average synaptic conductance.