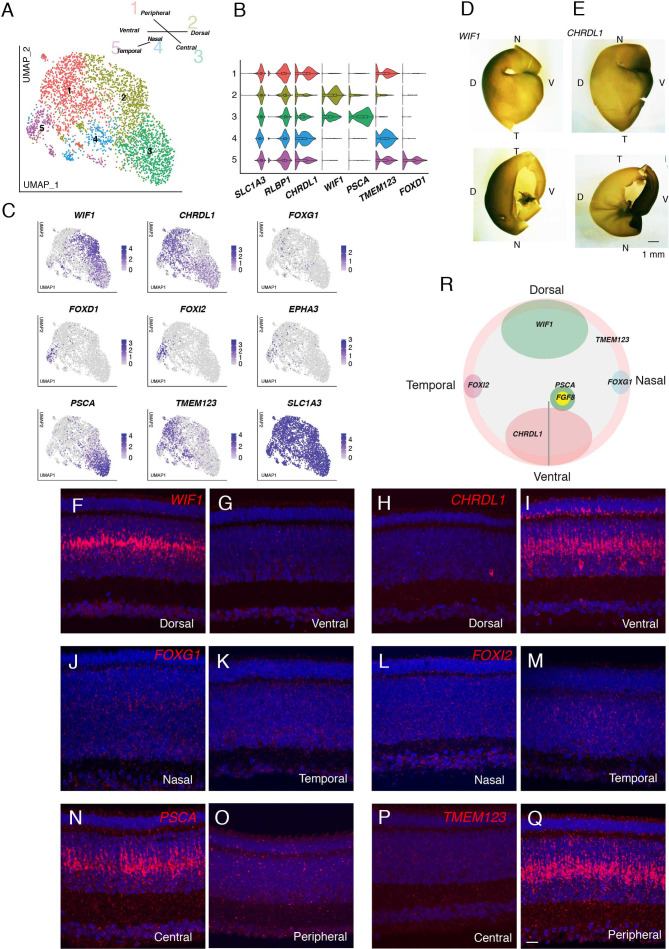
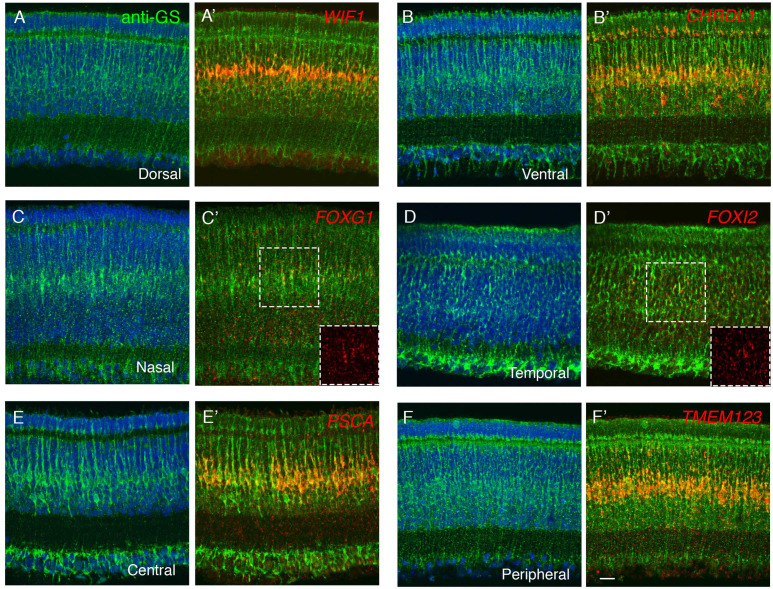
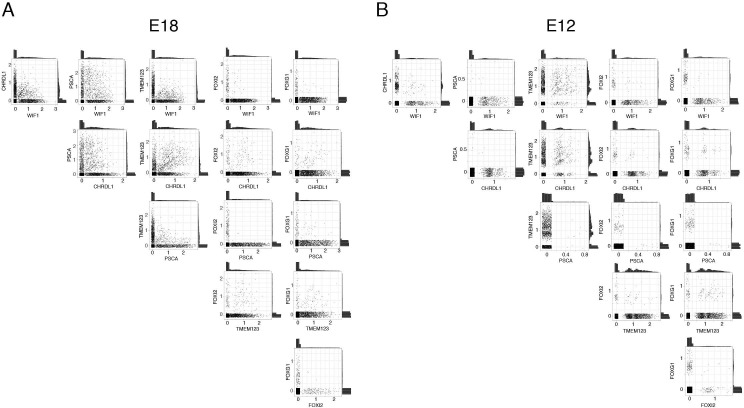
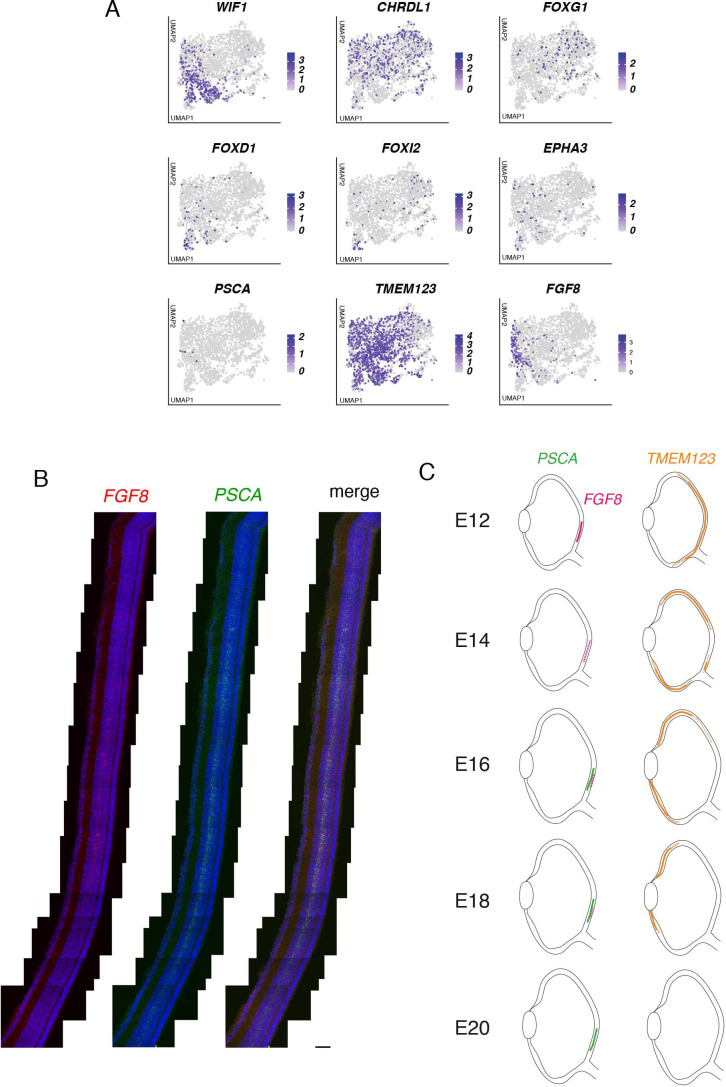
Figure 8. Transcriptomic map of topographic position in Müller glia.
(A) Clustering of E18 MGs using UMAP. Inset shows relationship between clusters and retinal position. (B,C) Violin (B) and feature (C) plots of genes differentially expressed among MG clusters. B also shows that pan-MG genes SLC1A3 and RLBP1 are expressed at similar levels among clusters. (D, E) In situ hybridization for WIF1 (D) and CHRDL1(E) on whole mounts at E13 photographed from the posterior (top panels) or anterior (bottom panels). The black structure at the ventral edge in the bottom panels is the intrinsically pigmented pecten oculi. Bar, 1 mm. (F–Q) In situ hybridization on sections from indicated retinal regions to show position-selective of genes from C in Müller glia. F-I WIF1 and CHRDL1 on E16 dorsal and ventral sections. CHRDL1 is also in a subset of amacrine cells throughout the retina. (J–M) FOXG1 and FOXI2 on E14 nasal and temporal sections. (N–Q) PSCA and TMEM123 on E16 central and peripheral sections. Bar, 10 µm. (R) Summary of position-dependent expression of genes in Müller glia at E16, based on images such as those in D-Q.