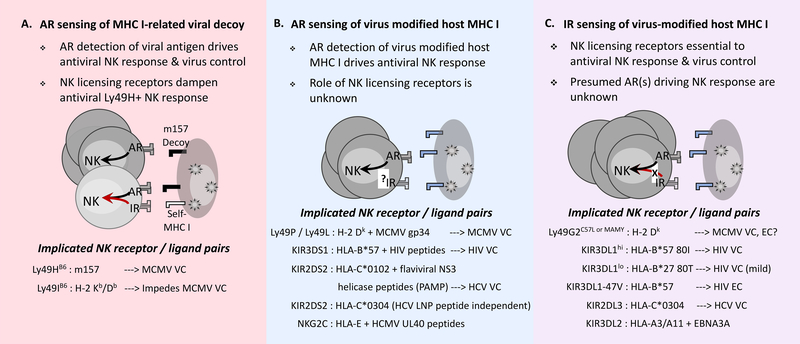
Figure 1. A proposed model for NK cell sensing of MHC I on virus infected target cells.
Proposed NK cell sensing modes involving activation (AR) or inhibitory (IR) receptor detection of viral targets with consequent effects on antiviral NK cells and host virus control (VC) are depicted. Major NK receptor signaling pathways implicated in each mode are shown. The extent of VC may vary and, in most cases, has not been compared across sensing modes. VC associated with high expression KIR3DL1hi, however, exceeds mild HIV protection noted for low expression KIR3DL1lo. Expression-independent KIR3DL1–47V is associated with HIV elite control (EC) in HLA-B*57 people. Self MHC I-dependent IR enhancement of AR sensing is represented by increased expansion of activated NK cells that are able to mediate highly efficient lysis of infected target cells.