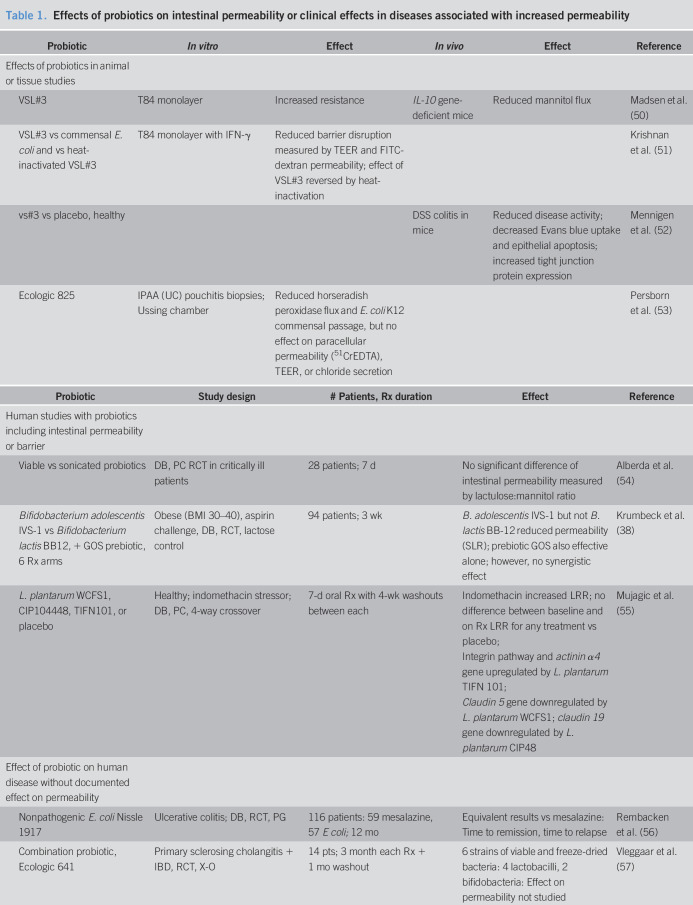
Table 1.
Effects of probiotics on intestinal permeability or clinical effects in diseases associated with increased permeability
| Probiotic | In vitro | Effect | In vivo | Effect | Reference |
| Effects of probiotics in animal or tissue studies | |||||
| VSL#3 | T84 monolayer | Increased resistance | IL-10 gene-deficient mice | Reduced mannitol flux | Madsen et al. (50) |
| VSL#3 vs commensal E. coli and vs heat-inactivated VSL#3 | T84 monolayer with IFN-γ | Reduced barrier disruption measured by TEER and FITC-dextran permeability; effect of VSL#3 reversed by heat-inactivation | Krishnan et al. (51) | ||
| vs#3 vs placebo, healthy | DSS colitis in mice | Reduced disease activity; decreased Evans blue uptake and epithelial apoptosis; increased tight junction protein expression | Mennigen et al. (52) | ||
| Ecologic 825 | IPAA (UC) pouchitis biopsies; Ussing chamber | Reduced horseradish peroxidase flux and E. coli K12 commensal passage, but no effect on paracellular permeability (51CrEDTA), TEER, or chloride secretion | Persborn et al. (53) |
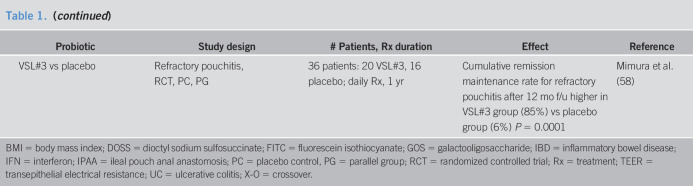
| Probiotic | Study design | # Patients, Rx duration | Effect | Reference |
| Human studies with probiotics including intestinal permeability or barrier | ||||
| Viable vs sonicated probiotics | DB, PC RCT in critically ill patients | 28 patients; 7 d | No significant difference of intestinal permeability measured by lactulose:mannitol ratio | Alberda et al. (54) |
| Bifidobacterium adolescentis IVS-1 vs Bifidobacterium lactis BB12, + GOS prebiotic, 6 Rx arms | Obese (BMI 30–40), aspirin challenge, DB, RCT, lactose control | 94 patients; 3 wk | B. adolescentis IVS-1 but not B. lactis BB-12 reduced permeability (SLR); prebiotic GOS also effective alone; however, no synergistic effect | Krumbeck et al. (38) |
| L. plantarum WCFS1, CIP104448, TIFN101, or placebo | Healthy; indomethacin stressor; DB, PC, 4-way crossover | 7-d oral Rx with 4-wk washouts between each | Indomethacin increased LRR; no difference between baseline and on Rx LRR for any treatment vs placebo; Integrin pathway and actinin α4 gene upregulated by L. plantarum TIFN 101; Claudin 5 gene downregulated by L. plantarum WCFS1; claudin 19 gene downregulated by L. plantarum CIP48 |
Mujagic et al. (55) |
| Effect of probiotic on human disease without documented effect on permeability | ||||
| Nonpathogenic E. coli Nissle 1917 | Ulcerative colitis; DB, RCT, PG | 116 patients: 59 mesalazine, 57 E coli; 12 mo | Equivalent results vs mesalazine: Time to remission, time to relapse | Rembacken et al. (56) |
| Combination probiotic, Ecologic 641 | Primary sclerosing cholangitis + IBD, RCT, X-O | 14 pts; 3 month each Rx + 1 mo washout | 6 strains of viable and freeze-dried bacteria: 4 lactobacilli, 2 bifidobacteria: Effect on permeability not studied | Vleggaar et al. (57) |
| VSL#3 vs placebo | Refractory pouchitis, RCT, PC, PG | 36 patients: 20 VSL#3, 16 placebo; daily Rx, 1 yr | Cumulative remission maintenance rate for refractory pouchitis after 12 mo f/u higher in VSL#3 group (85%) vs placebo group (6%) P = 0.0001 | Mimura et al. (58) |
BMI = body mass index; DOSS = dioctyl sodium sulfosuccinate; FITC = fluorescein isothiocyanate; GOS = galactooligosaccharide; IBD = inflammatory bowel disease; IFN = interferon; IPAA = ileal pouch anal anastomosis; PC = placebo control, PG = parallel group; RCT = randomized controlled trial; Rx = treatment; TEER = transepithelial electrical resistance; UC = ulcerative colitis; X-O = crossover.