Fig. 1.
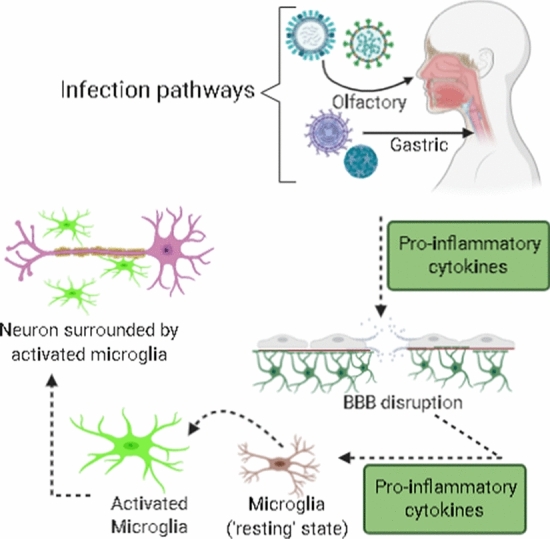
Pathological agents may infect the organism by different pathways, such as olfactory and gastric. These pathogens trigger a cascade of inflammatory responses (increased levels of cytokines, for example) that disrupt the BBB, activate microglia, and lead to a subsequent clustering around neuronal cells, resulting in neuronal damage.
Source: adapted from Limphaibool et al. (2019) [71]
