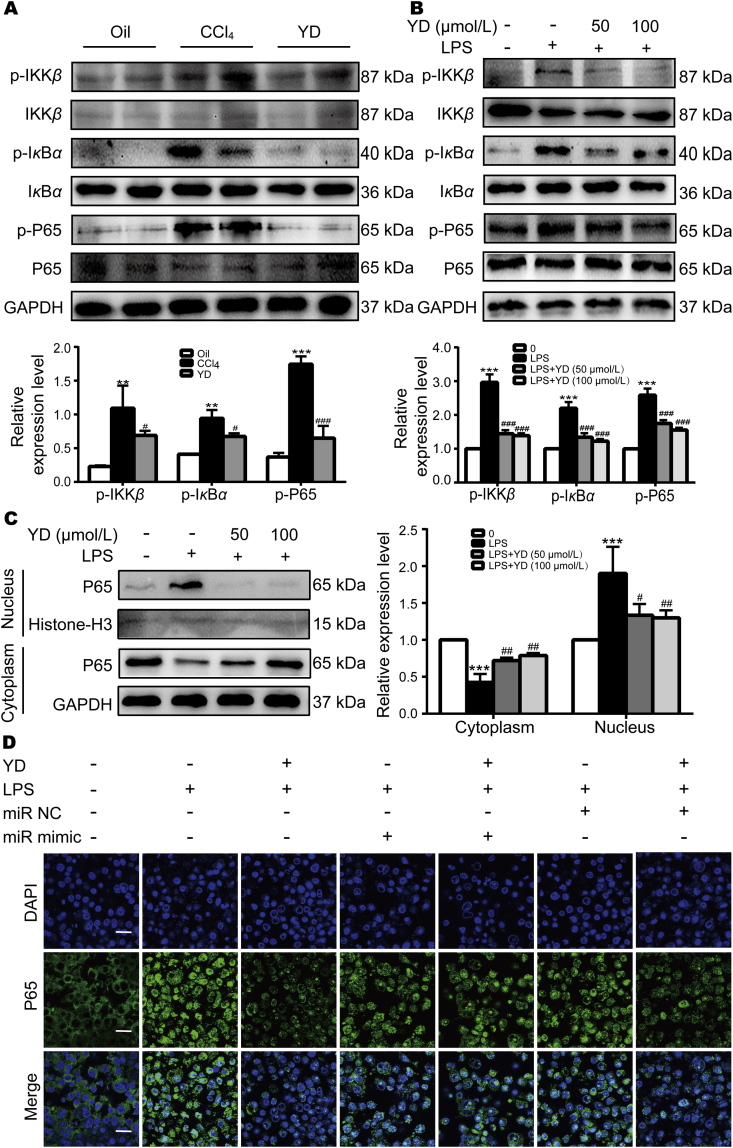
Figure 6.
YD significantly inhibited NF-κB pathway in vivo and in vitro. (A) YD inhibited NF-κB pathway in the CCl4-induced mice (mean ± SD, n = 6). ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs. the oil group; #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001 vs. the CCl4-induced group. (B) YD inhibited NF-κB pathway in the LPS-induced RAW264.7 cells (mean ± SD, n = 3). ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs. control; ###P < 0.001 vs. LPS-induced group (without YD). (C) The protein expression levels of P65 in the cytosol and nucleus were examined by Western blotting (mean ± SD, n = 3). Histone-H3 is an internal reference indicator of the nucleus, and the nucleus protein expression levels are normalized to Histone-H3 levels. ∗∗∗P < 0.001 vs. control; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. LPS-induced group (without YD). (D) Nuclear translocation of P65 in RAW264.7 cells with overexpressing miR-155 mimic or its control was assayed by immunofluorescence (scale bar, 20 μm).