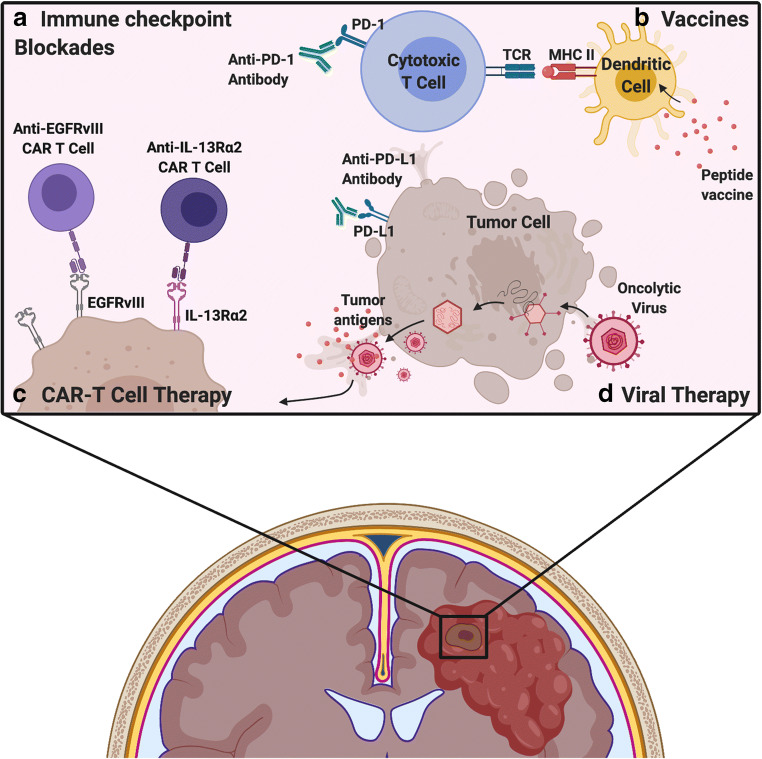
Fig. 2.
Immunotherapeutic strategies for treatment of glioblastoma. a Immune checkpoint receptor/ligands such as PD-1 expressed on T cells and PD-L1 expressed on tissue cells downregulate the adaptive immune response in normal tissues. Tumors may express PD-L1 as well, thus inhibiting T cell activation in tumors. Immune checkpoint inhibitors are antibodies that block receptor-ligand interactions, such as between PD-1 and PD-L1, thus inhibiting the immunosuppressive effects of this interaction. b Vaccines introduce GBM-specific antigens to native APCs including dendritic cells and rely on MHC-dependent presentation to T cells to stimulate a GBM-targeted immune response. c CAR-T cell therapy uses autologous T cells, which are genetically modified to target GBM-specific surface antigens, such as EGFRvIII and IL-13Rα2. Unlike vaccines, CAR-T cells do not rely on MHC-dependent antigen presentation. d Viral therapy encompasses the use of oncolytic viruses and retroviruses to either initiate tumor cell lysis and release of tumor antigen or to integrate therapeutic transgenes for expression by the tumor cell