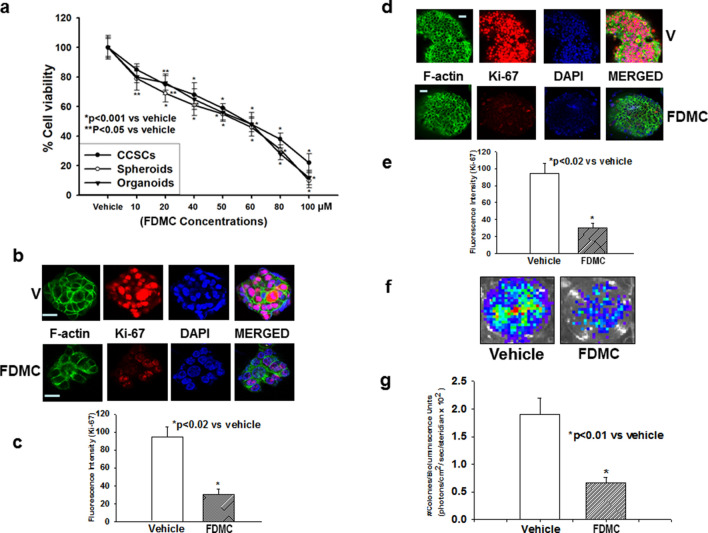
Figure 1.
Effects of FDMC on growth of human colon cancer stem cells (CD24+, CD44+, LGR5+), spheroids, and organoids, as evidenced by comparisons with vehicle-treated controls (V = vehicle). (a) FDMC significantly inhibited cell viability of human CCSCs, spheroids, and organoids in a concentration-dependent manner (CellTiter Glo assay). (b,c) Confocal microscopy data show that FDMC (50 µM) significantly inhibited proliferation (Ki-67 red immunofluorescence staining) in spheroids (*p < 0.02). (d,e) Confocal microscopy data show that FDMC (50 µM) significantly inhibited proliferation (Ki-67 red immunofluorescence staining) in organoids (*p < 0.02). (f,g) Colonogenic soft agar assay with luciferase-expressing CCSCs shows that FDMC (50 µM) significantly inhibited anchorage-independent growth (luminescence units) (*p < 0.01). Results are mean ± standard error of the means (bars; n = 3).